OPCML is a broad tumor suppressor for multiple carcinomas and lymphomas with frequently epigenetic inactivation
- PMID: 18714356
- PMCID: PMC2500176
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0002990
OPCML is a broad tumor suppressor for multiple carcinomas and lymphomas with frequently epigenetic inactivation
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2008;3(9). doi: 10.1371/annotation/f394b95b-c731-41a3-b0dc-be25fb6a227c
Abstract
Background: Identification of tumor suppressor genes (TSGs) silenced by CpG methylation uncovers the molecular mechanism of tumorigenesis and potential tumor biomarkers. Loss of heterozygosity at 11q25 is common in multiple tumors including nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC). OPCML, located at 11q25, is one of the downregulated genes we identified through digital expression subtraction.
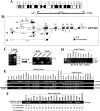
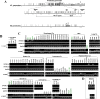
Methodology/principal findings: Semi-quantitative RT-PCR showed frequent OPCML silencing in NPC and other common tumors, with no homozygous deletion detected by multiplex differential DNA-PCR. Instead, promoter methylation of OPCML was frequently detected in multiple carcinoma cell lines (nasopharyngeal, esophageal, lung, gastric, colon, liver, breast, cervix, prostate), lymphoma cell lines (non-Hodgkin and Hodgkin lymphoma, nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma) and primary tumors, but not in any non-tumor cell line and seldom weakly methylated in normal epithelial tissues. Pharmacological and genetic demethylation restored OPCML expression, indicating a direct epigenetic silencing. We further found that OPCML is stress-responsive, but this response is epigenetically impaired when its promoter becomes methylated. Ecotopic expression of OPCML led to significant inhibition of both anchorage-dependent and -independent growth of carcinoma cells with endogenous silencing.
Conclusions/significance: Thus, through functional epigenetics, we identified OPCML as a broad tumor suppressor, which is frequently inactivated by methylation in multiple malignancies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Baylin SB, Ohm JE. Epigenetic gene silencing in cancer - a mechanism for early oncogenic pathway addiction? Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Jones PA, Baylin SB. The fundamental role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2002;3:415–428. - PubMed
-
- Belinsky SA. Gene-promoter hypermethylation as a biomarker in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:707–717. - PubMed
-
- Tao Q, Chan AT. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: molecular pathogenesis and therapeutic developments. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2007;9:1–24. - PubMed
-
- Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus in the pathogenesis of NPC. Semin Cancer Biol. 2002;12:431–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

