Primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma in a baboon (Papio sp.)
- PMID: 18715267
- PMCID: PMC2758419
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0684.2008.00304.x
Primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma in a baboon (Papio sp.)
Abstract
Background: Primary neuroendocrine carcinomas of the liver have rarely been reported in humans and domestic animals, but not in non-human primates.
Methods: We describe the morphologic and immunohistochemical features of a primary hepatic neuroendocrine carcinoma found in a 29-year-old female baboon.
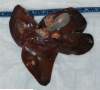
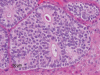
Results and conclusions: The neoplasm was characterized by multiple solid nodules that were multifocally distributed in the liver. Metastases were not observed. Histologically, the neoplasm was composed of cords and nests of epithelial cells arranged in a neuroendocrine pattern, occasionally forming glandular and rosette-like structures. On immunohistochemical evaluation, the neoplastic cells were immunopositive for pancytokeratin, chromogranin A, neuron-specific endolase, and synaptophysin and were negative for vimentin, S100 protein, glucagon, and insulin.
Figures

References
-
- Cianciolo RE, Butler SD, Eggers JS, Dick EJ, Jr, Leland M, De la Garza M, Brasky KM, Cummins LB, Hubbard GB. Spontaneous neoplasia in the baboon (Papio spp.). J Med Primatol. 2007;36:61–79. - PubMed
-
- Cianciolo RE, Hubbard GB. A review of spontaneous neoplasia in baboons (Papio spp.). J Med Primatol. 2005;34:51–66. - PubMed
-
- Kaya G, Pasche C, Osterheld MC, Chaubert P, Fontolliet C. Primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the liver: an autopsy case. Pathol Int. 2001;51:874–8. - PubMed
-
- Klöppel G. Tumor biology and histopathology of neuroendocrine tumors. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;21:15–31. - PubMed
-
- Libbrecht L, Roskams T. Hepatic progenitor cells in human liver diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2002;13:389–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

