Motexafin gadolinium and involved field radiation therapy for intrinsic pontine glioma of childhood: a Children's Oncology Group phase I study
- PMID: 18715950
- PMCID: PMC2666252
- DOI: 10.1215/15228517-2008-043
Motexafin gadolinium and involved field radiation therapy for intrinsic pontine glioma of childhood: a Children's Oncology Group phase I study
Abstract
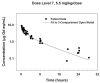
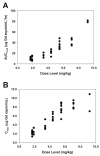
The purpose of this study was to determine the dose-limiting toxicities, maximum tolerated dose, pharmacokinetics, and intratumor and brain distribution of motexafin gadolinium (MGd) with involved field radiation therapy in children with newly diagnosed intrinsic pontine gliomas. MGd was administered as a 5-min intravenous bolus 2-5 h prior to standard radiation. The starting dose was 1.7 mg/kg. After first establishing that 5 doses/week for 6 weeks was tolerable, the dose of MGd was escalated until dose-limiting toxicity was reached. Radiation therapy was administered to 54 Gy in 30 once-daily fractions. Forty-four children received MGd at doses of 1.7 to 9.2 mg/kg daily prior to radiation therapy for 6 weeks. The maximum tolerated dose was 4.4 mg/kg. The primary dose-limiting toxicities were grade 3 and 4 hypertension and elevations in serum transaminases. Median elimination half-life and clearance values were 6.6 h and 25.4 ml/kg/h, respectively. The estimated median survival was 313 days (95% confidence interval, 248-389 days). The maximum tolerated dose of MGd and the recommended phase II dose was 4.4 mg/kg when administered as a daily intravenous bolus in conjunction with 6 weeks of involved field radiation therapy for pediatric intrinsic pontine gliomas.
Figures
References
-
- Jallo GI, Biser-Rohrbaugh A, Freed D. Brainstem gliomas. Childs Nerv Syst. 2004;20:143–153. - PubMed
-
- Smith MA, Freidlin B, Ries LA, et al. Trends in reported incidence of primary malignant brain tumors in children in the United States. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90:1269–1277. - PubMed
-
- Donaldson SS, Laningham F, Fisher PG. Advances toward an understanding of brainstem gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:1266–1272. - PubMed
-
- Albright AL, Guthkelch AN, Packer RJ, et al. Prognostic factors in pediatric brain-stem gliomas. J Neurosurg. 1986;65:751–755. - PubMed
-
- Fisher PG, Breiter SN, Carson BS, et al. A clinicopathologic reappraisal of brain stem tumor classification. Identification of pilocystic astrocytoma and fibrillary astrocytoma as distinct entities. Cancer. 2000;89:1569–1576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources