CLASP modulates microtubule-cortex interaction during self-organization of acentrosomal microtubules
- PMID: 18716054
- PMCID: PMC2575154
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e08-06-0665
CLASP modulates microtubule-cortex interaction during self-organization of acentrosomal microtubules
Abstract
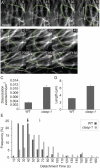
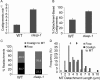
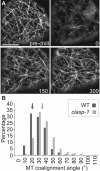
CLASP proteins associate with either the plus ends or sidewalls of microtubules depending on the subcellular location and cell type. In plant cells, CLASP's distribution along the full length of microtubules corresponds with the uniform anchorage of microtubules to the cell cortex. Using live cell imaging, we show here that loss of CLASP in Arabidopsis thaliana results in partial detachment of microtubules from the cortex. The detached portions undergo extensive waving, distortion, and changes in orientation, particularly when exposed to the forces of cytoplasmic streaming. These deviations from the normal linear polymerization trajectories increase the likelihood of intermicrotubule encounters that are favorable for subsequent bundle formation. Consistent with this, cortical microtubules in clasp-1 leaf epidermal cells are hyper-parallel. On the basis of these data, we identify a novel mechanism where modulation of CLASP activity governs microtubule-cortex attachment, thereby contributing to self-organization of cortical microtubules.
Figures
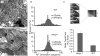


References
-
- Akhmanova A., et al. Clasps are CLIP-115 and -170 associating proteins involved in the regional regulation of microtubule dynamics in motile fibroblasts. Cell. 2001;104:923–935. - PubMed
-
- Bartolini F., Gundersen G. G. Generation of noncentrosomal microtubule arrays. J. Cell Sci. 2006;119:4155–4163. - PubMed
-
- Chan J., Calder G. M., Doonan J. H., Lloyd C. W. EB1 reveals mobile microtubule nucleation sites in Arabidopsis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003;5:967–971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

