Dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors are essential for the arousal effect of modafinil
- PMID: 18716204
- PMCID: PMC6671058
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1819-08.2008
Dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors are essential for the arousal effect of modafinil
Abstract
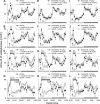
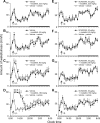
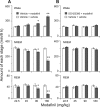
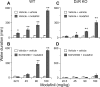
Modafinil is a wake-promoting compound with low abuse potential used in the treatment of narcolepsy. Although the compound is reported to affect multiple neurotransmitter systems such as catecholamines, serotonin, glutamate, GABA, orexin, and histamine, however, the molecular mechanism by which modafinil increases wakefulness is debated. Herein we used dopamine (DA) D(2) receptor (D(2)R)-deficient mice combined with D(1)R- and D(2)R-specific antagonists to clarify the role of DA receptors in the arousal effects of modafinil. In wild-type mice, intraperitoneal modafinil induced wakefulness in a dose-dependent manner. Pretreatment with either D(1)R antagonist SCH23390 [R-(+)-7-chloro-8-hydroxy-3-methyl-1-phenyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1H-3-benzazepine] at 30 microg/kg or D(2)R antagonist raclopride at 2 mg/kg blocked the arousal effects of low-dose modafinil at 22.5 and 45 mg/kg. When modafinil was given at 90 and 180 mg/kg, pretreatment of D(1)R antagonist did not affect the wakefulness at all, whereas D(2)R antagonist significantly attenuated the wakefulness to the half level compared with vehicle control. Similarly, D(2)R knock-out (KO) mice exhibited attenuated modafinil-induced wakefulness. However, pretreatment of D(2)R KO mice with D(1)R antagonist completely abolished arousal effects of modafinil. These findings strongly indicate that dopaminergic D(1)R and D(2)R are essential for the wakefulness induced by modafinil.
Figures


Comment in
-
Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor family contributions to modafinil-induced wakefulness.J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 4;29(9):2663-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5843-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19261860 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Roles of adrenergic α1 and dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the mediation of the desynchronization effects of modafinil in a mouse EEG synchronization model.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 7;8(10):e76102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076102. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116090 Free PMC article.
-
Essential role of dopamine D2 receptor in the maintenance of wakefulness, but not in homeostatic regulation of sleep, in mice.J Neurosci. 2010 Mar 24;30(12):4382-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4936-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20335474 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D1 and D2 receptor family contributions to modafinil-induced wakefulness.J Neurosci. 2009 Mar 4;29(9):2663-5. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5843-08.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19261860 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
What keeps us awake: the neuropharmacology of stimulants and wakefulness-promoting medications.Sleep. 2004 Sep 15;27(6):1181-94. doi: 10.1093/sleep/27.6.1181. Sleep. 2004. PMID: 15532213 Review.
-
Action of modafinil through histaminergic and orexinergic neurons.Vitam Horm. 2012;89:259-78. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-394623-2.00014-7. Vitam Horm. 2012. PMID: 22640618 Review.
Cited by
-
Addiction-related gene regulation: risks of exposure to cognitive enhancers vs. other psychostimulants.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jan;100:60-80. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2012.10.001. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23085425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ablation of Ventral Midbrain/Pons GABA Neurons Induces Mania-like Behaviors with Altered Sleep Homeostasis and Dopamine D2R-mediated Sleep Reduction.iScience. 2020 Jun 26;23(6):101240. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101240. Epub 2020 Jun 4. iScience. 2020. PMID: 32563157 Free PMC article.
-
A rare case of modafinil dependence presenting as sleep disorder.Ind Psychiatry J. 2021 Oct;30(Suppl 1):S354-S355. doi: 10.4103/0972-6748.328856. Epub 2021 Oct 22. Ind Psychiatry J. 2021. PMID: 34908736 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Drug-induced sleep: theoretical and practical considerations.Pflugers Arch. 2012 Jan;463(1):177-86. doi: 10.1007/s00424-011-1033-3. Epub 2011 Sep 28. Pflugers Arch. 2012. PMID: 21953011 Review.
-
Roles of adrenergic α1 and dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the mediation of the desynchronization effects of modafinil in a mouse EEG synchronization model.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 7;8(10):e76102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076102. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24116090 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aizman O, Brismar H, Uhlén P, Zettergren E, Levey AI, Forssberg H, Greengard P, Aperia A. Anatomical and physiological evidence for D1 and D2 dopamine receptor colocalization in neostriatal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:226–230. - PubMed
-
- Akaoka H, Roussel B, Lin JS, Chouvet G, Jouvet M. Effect of modafinil and amphetamine on the rat catecholaminergic neuron activity. Neurosci Lett. 1991;123:20–22. - PubMed
-
- Billiard M, Besset A, Montplaisir J, Laffont F, Goldenberg F, Weill JS, Lubin S. Modafinil: a double-blind multicentric study. Sleep. 1994;17:S107–S112. - PubMed
-
- Chemelli RM, Willie JT, Sinton CM, Elmquist JK, Scammell T, Lee C, Richardson JA, Williams SC, Xiong Y, Kisanuki Y, Fitch TE, Nakazato M, Hammer RE, Saper CB, Yanagisawa M. Narcolepsy in orexin knockout mice: molecular genetics of sleep regulation. Cell. 1999;98:437–451. - PubMed
-
- Deroche-Gamonet V, Darnaudéry M, Bruins-Slot L, Piat F, Le Moal M, Piazza PV. Study of the addictive potential of modafinil in naive and cocaine-experienced rats. Psychopharmacology. 2002;161:387–395. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
