Sister chromatid cohesion role for CDC28-CDK in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 18716324
- PMCID: PMC2535721
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.108.092288
Sister chromatid cohesion role for CDC28-CDK in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
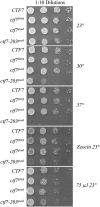
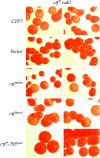
High-fidelity chromosome segregation requires that the sister chromatids produced during S phase also become paired during S phase. Ctf7p (Eco1p) is required to establish sister chromatid pairing specifically during DNA replication. However, Ctf7p also becomes active during G2/M in response to DNA damage. Ctf7p is a phosphoprotein and an in vitro target of Cdc28p cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK), suggesting one possible mechanism for regulating the essential function of Ctf7p. Here, we report a novel synthetic lethal interaction between ctf7 and cdc28. However, neither elevated CDC28 levels nor CDC28 Cak1p-bypass alleles rescue ctf7 cell phenotypes. Moreover, cells expressing Ctf7p mutated at all full- and partial-consensus CDK-phosphorylation sites exhibit robust cell growth. These and other results reveal that Ctf7p regulation is more complicated than previously envisioned and suggest that CDK acts in sister chromatid cohesion parallel to Ctf7p reactions.
Figures






References
-
- Antoniacci, L. M., and R. V. Skibbens, 2006. Sister-chromatid telomere cohesion is nonredundant and resists both spindle forces and telomere motility. Curr. Biol. 16 902–906. - PubMed
-
- Blat, Y., and N. Kleckner, 1999. Cohesins bind to preferential sites along yeast chromosome III, with differential regulation along arms versus the centric region. Cell 98 249–259. - PubMed
-
- Boeke, J. D., J. Trueheart, G. Natsoulis and G. R. Fink, 1987. 5-Flouoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 154 164–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

