Effect of microneedle design on pain in human volunteers
- PMID: 18716497
- PMCID: PMC2917250
- DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e31816778f9
Effect of microneedle design on pain in human volunteers
Abstract
Objectives: To design microneedles that minimize pain, this study tested the hypothesis that microneedles cause significantly less pain than a 26-gauge hypodermic needle, and that decreasing microneedle length and the number of microneedles reduces pain in normal human volunteers.
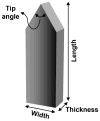
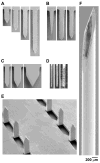
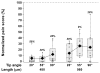
Methods: Single microneedles with lengths ranging from 480 to 1450 microm, widths from 160 to 465 microm, thicknesses from 30 to 100 microm, and tip angles from 20 to 90 degrees; and arrays containing 5 or 50 microneedles were inserted into the volar forearms of 10 healthy, human volunteers in a double-blinded, randomized study. Visual analog scale pain scores were recorded and compared with each other and to the pain from a 26-gauge hypodermic needle.
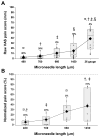
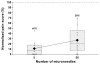
Results: All microneedles investigated were significantly less painful than the hypodermic needle with microneedle pain scores varying from 5% to 40% of the hypodermic needle. Microneedle length had the strongest effect on pain, where a 3-fold increase in length increased the pain score by 7-fold. The number of microneedles also affected the pain score, where a 10-fold increase in the number of microneedles increased pain just over 2-fold. Microneedle tip angle, thickness, and width did not significantly influence pain.
Discussion: Microneedles are significantly less painful than a 26-gauge hypodermic needle over the range of dimensions investigated. Decreasing microneedle length and number of microneedles reduces pain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid local anesthesia in humans using minimally invasive microneedles.Clin J Pain. 2012 Feb;28(2):129-35. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0b013e318225dbe9. Clin J Pain. 2012. PMID: 21712713 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
In vivo assessment of safety of microneedle arrays in human skin.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008 Oct 2;35(3):193-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2008.06.016. Epub 2008 Jul 8. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008. PMID: 18657610
-
The Effect of Microneedle Thickness on Pain During Minimally Invasive Facial Procedures: A Clinical Study.Aesthet Surg J. 2014 Jul;34(5):757-65. doi: 10.1177/1090820X14532941. Epub 2014 Jul 1. Aesthet Surg J. 2014. PMID: 24787992 Clinical Trial.
-
Needle size for vaccination procedures in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 9;8(8):CD010720. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010720.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30091147 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle-based vaccines.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009;333:369-93. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-92165-3_18. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19768415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Microneedle System Coated with Hydrogels Containing Protoporphyrin IX for Potential Application in Pharmaceutical Technology.Methods Protoc. 2024 Sep 13;7(5):73. doi: 10.3390/mps7050073. Methods Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39311374 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle-Based Delivery: An Overview of Current Applications and Trends.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Jun 19;12(6):569. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12060569. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32575392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Integrated Transdermal Drug Delivery System with Micropump and Microneedle Made from Polymers.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Dec 27;14(1):71. doi: 10.3390/mi14010071. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36677132 Free PMC article.
-
Coated microneedle-based cutaneous immunotherapy prevents Der p 1-induced airway allergy in mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Dec;142(6):2007-2011.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.08.017. Epub 2018 Aug 30. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30171871 Free PMC article.
-
Microneedle Patch for Painless Intradermal Collection of Interstitial Fluid Enabling Multianalyte Measurement of Small Molecules, SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies, and Protein Profiling.Adv Healthc Mater. 2023 May;12(13):e2202564. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202202564. Epub 2023 Feb 21. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023. PMID: 36748807 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Prausnitz MR. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004;56(5):581–7. - PubMed
-
- Hanas R. Reducing injection pain in children and adolescents with diabetes: a review of indwelling catheters. Pediatr Diabetes. 2004;5(2):102–11. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton JG. Needle phobia: a neglected diagnosis. J Fam Pract. 1995;41(2):169–75. - PubMed
-
- Deacon B, Abramowitz J. Fear of needles and vasovagal reactions among phlebotomy patients. J Anxiety Disord. 2006;20(7):946–60. - PubMed
-
- Nir Y, Paz A, Sabo E, Potasman I. Fear of injections in young adults: prevalence and associations. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68(3):341–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

