Corin: new insights into the natriuretic peptide system
- PMID: 18716601
- PMCID: PMC2655200
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2008.418
Corin: new insights into the natriuretic peptide system
Abstract
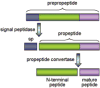
Natriuretic peptides are important in regulating salt and body-fluid balance. In cells, these peptides are made as precursor forms that are converted to active forms by proteolyic processing. Corin is a transmembrane serine protease identified in the heart. Corin converts pro-atrial natriuretic peptide (pro-ANP) to active ANP in a sequence-specific manner. In mice, lack of corin prevents the conversion of pro-ANP to ANP and causes salt-sensitive hypertension. The hypertensive phenotype is exacerbated when the mice become pregnant. In humans, single nucleotide polymorphisms in the corin gene have been identified in African Americans with hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy. These data indicate that corin is important in maintaining normal blood pressure in vivo and that corin deficiency may contribute to hypertension and heart disease in patients.
Figures

References
-
- de Bold AJ, Borenstein HB, Veress AT, Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981;28:89–94. - PubMed
-
- Tervonen V, Arjamaa O, Kokkonen K, Ruskoaho H, Vuolteenaho O. A novel cardiac hormone related to A-, B- and C-type natriuretic peptides. Endocrinology. 1998;139:4021–4025. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada T, Takei Y. Integrative approach to osmoregulatory action of atrial natriuretic peptide in seawater eels. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2006;147:31–38. - PubMed
-
- Lee CY, Burnett JC., Jr Natriuretic peptides and therapeutic applications. Heart Fail Rev. 2007;12:131–142. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

