Nuclear receptor signalling in dendritic cells connects lipids, the genome and immune function
- PMID: 18716631
- PMCID: PMC2525841
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2008.160
Nuclear receptor signalling in dendritic cells connects lipids, the genome and immune function
Abstract
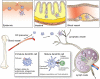
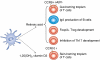
Dendritic cells (DCs) are sentinels of the immune system and represent a heterogeneous cell population. The existence of distinct DC subsets is due to their inherent plasticity and to the changing microenvironment modulating their immunological properties. Numerous signalling pathways have impacts on DCs. It appears that besides cytokines/chemokines, lipid mediators also have profound effects on the immunogenicity of DCs. Some of these lipid mediators exert an effect through nuclear hormone receptors. Interestingly, more recent findings suggest that DCs are able to convert precursors to active hormones, ligands for nuclear receptors. Some of these DC-derived lipids, in particular retinoic acid (RA), have a central function in shaping T-cell development and effector functions. In this review, we summarize and highlight the function of a set of nuclear receptors (PPARgamma, RA receptor, vitamin D receptor and glucocorticoid receptor) in DC biology. Defining the contribution of nuclear hormone receptor signalling in DCs can help one to understand the regulatory logic of lipid signalling and allow the exploitation of their potential for therapeutic intervention in various immunological diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Abe M, Thomson AW (2003) Influence of immunosuppressive drugs on dendritic cells. Transpl Immunol 11: 357–365 - PubMed
-
- Angeli V, Hammad H, Staels B, Capron M, Lambrecht BN, Trottein F (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma inhibits the migration of dendritic cells: consequences for the immune response. J Immunol 170: 5295–5301 - PubMed
-
- Angeli V, Llodra J, Rong JX, Satoh K, Ishii S, Shimizu T, Fisher EA, Randolph GJ (2004) Dyslipidemia associated with atherosclerotic disease systemically alters dendritic cell mobilization. Immunity 21: 561–574 - PubMed
-
- Appel S, Mirakaj V, Bringmann A, Weck MM, Grunebach F, Brossart P (2005) PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit toll-like receptor mediated activation of dendritic cells via the MAP kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Blood 106: 3888–3894 - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J, Steinman RM (1998) Dendritic cells and the control of immunity. Nature 392: 245–252 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

