Cytomegalovirus vaccines fail to induce epithelial entry neutralizing antibodies comparable to natural infection
- PMID: 18718497
- PMCID: PMC2583261
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.07.092
Cytomegalovirus vaccines fail to induce epithelial entry neutralizing antibodies comparable to natural infection
Abstract
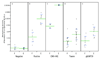
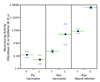
Antibodies that neutralize cytomegalovirus (CMV) entry into fibroblasts are predominantly directed against epitopes within virion glycoproteins that are required for attachment and entry. However, the mechanism of CMV entry into epithelial and endothelial cells differs from fibroblast entry. Using assays that simultaneously measured neutralizing activities against CMV entry into fibroblasts and epithelial cells, we found that human immune sera and CMV-hyperimmuneglobulins have on on average 48-fold higher neutralizing activities against epithelial cell entry compared to fibroblast entry, suggesting that natural CMV infections elicit neutralizing antibodies that are epithelial entry-specific. This activity could not be adsorbed with recombinant gB. The Towne vaccine and the gB/MF59 subunit vaccine induced epithelial entry-specific neutralizing activities that were on on average 28-fold (Towne) or 15-fold (gB/MF59) lower than those observed following natural infection. These results suggest that CMV vaccine efficacy may be enhanced by the induction of epithelial entry-specific neutralizing antibodies.
Figures

References
-
- Fowler KB, Stagno S, Pass RF, Britt WJ, Boll TJ, Alford CA. The outcome of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in relation to maternal antibody status. N Engl J Med. 1992;326(10):663–667. - PubMed
-
- Stratton KR, Durch SJ, Lawrence RS, editors. Vaccines for the 21st Century: A Tool for Decisionmaking. Washingto D.C: National Academy Press; 2000. - PubMed
-
- Marshall GS, Rabalais GP, Stout GG, Waldeyer SL. Antibodies to recombinant-derived glycoprotein B after natural human cytomegalovirus infection correlate with neutralizing activity. J Infect Dis. 1992;165(2):381–384. - PubMed
-
- Urban M, Klein M, Britt WJ, Hassfurther E, Mach M. Glycoprotein H of human cytomegalovirus is a major antigen for the neutralizing humoral immune response. J Gen Virol. 1996;77(Pt 7):1537–1547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

