Protein modifications in transcription elongation
- PMID: 18718879
- PMCID: PMC2641038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2008.07.008
Protein modifications in transcription elongation
Abstract
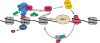
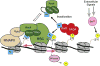
Posttranslational modifications (PTMs) of proteins play essential roles in regulating signaling, protein-protein modifications and subcellular localization. In this review, we focus on posttranslational modification of histones and RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) and their roles in gene transcription. A survey of the basic features of PTMs is provided followed by a more detailed account of how PTMs on histones and RNAPII regulate transcription in the model organism Saccharomyces cerevisiae. We emphasize the interconnections between histone and RNAPII PTMs and speculate upon the larger role PTMs have in regulating protein function in the cell.
Figures

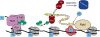
References
-
- Black DL. Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:291–336. - PubMed
-
- Maniatis T, Tasic B. Alternative pre-mRNA splicing and proteome expansion in metazoans. Nature. 2002;418:236–243. - PubMed
-
- Uy R, Wold F. Posttranslational covalent modification of proteins. Science. 1977;198:890–896. - PubMed
-
- Walsh CT. Posttranslational modifications of proteins: expanding nature's inventory. Roberts and Co.; Englewood, CO: 2006.
-
- Dunlop PC, Bodley JW. Biosynthetic labeling of diphthamide in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:4754–4758. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

