Leptin stimulates both JAK2-dependent and JAK2-independent signaling pathways
- PMID: 18718905
- PMCID: PMC2568905
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805545200
Leptin stimulates both JAK2-dependent and JAK2-independent signaling pathways
Abstract
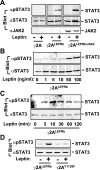
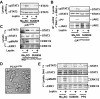
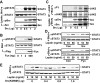
Leptin controls body weight by activating the long form of the leptin receptor (LEPRb). Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) is associated with LEPRb and autophosphorylates in response to leptin. JAK2 also phosphorylates LEPRb, STAT3, and multiple other downstream molecules. Surprisingly, here we show that JAK2 is not required for leptin stimulation of STAT3 phosphorylation. Leptin time- and dose-dependently stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of STAT3 in both human and mouse JAK2-null cells. Leptin also increased the viability of JAK2-null cells. Overexpression of c-Src or Fyn, two Src family members, promoted STAT3 phosphorylation, whereas inhibition of the endogenous Src family members by either pharmacological inhibitors or dominant negative Src(K298M) decreased the ability of leptin to stimulate the phosphorylation of STAT3 and ERK1/2. Leptin also stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of kinase-inactive JAK2(K882E) in JAK2-null cells. Overexpression of JAK2(K882E) enhanced the ability of leptin to stimulate STAT3 phosphorylation in JAK2-null cells. Tyr1138 in LEPRb was required for leptin-stimulated phosphorylation of STAT3 but not JAK2(K882E). These data suggest that leptin stimulates non-JAK2 tyrosine kinase(s), including the Src family members, which phosphorylate JAK2, STAT3, and other molecules downstream of LEPRb. JAK2 mediates leptin signaling by both phosphorylating its substrates and forming a signaling complex as a scaffolding/adaptor protein. The non-JAK2 kinase(s) and JAK2 may act coordinately and synergistically to mediate leptin response.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Glucose enhances leptin signaling through modulation of AMPK activity.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031636. Epub 2012 Feb 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22359610 Free PMC article.
-
SH2B1 enhances leptin signaling by both Janus kinase 2 Tyr813 phosphorylation-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Mol Endocrinol. 2007 Sep;21(9):2270-81. doi: 10.1210/me.2007-0111. Epub 2007 Jun 12. Mol Endocrinol. 2007. PMID: 17565041
-
15-Lipoxygenase-1-enhanced Src-Janus kinase 2-signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 stimulation and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression require redox-sensitive activation of epidermal growth factor receptor in vascular wall remodeling.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jun 24;286(25):22478-88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225060. Epub 2011 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21536676 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin receptor signaling and the regulation of mammalian physiology.Int J Obes (Lond). 2008 Dec;32 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):S8-12. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2008.232. Int J Obes (Lond). 2008. PMID: 19136996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009 Dec;297(6):E1247-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00274.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 1. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009. PMID: 19724019 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Role of Lck in Leptin-Induced Inflammation and Implications for Renal Aging.Aging Dis. 2019 Dec 1;10(6):1174-1186. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0218. eCollection 2019 Dec. Aging Dis. 2019. PMID: 31788330 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin Controls Glutamatergic Synaptogenesis and NMDA-Receptor Trafficking via Fyn Kinase Regulation of NR2B.Endocrinology. 2020 Feb 1;161(2):bqz030. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqz030. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 31840160 Free PMC article.
-
A Potential Nutraceutical Candidate Lactucin Inhibits Adipogenesis through Downregulation of JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway-Mediated Mitotic Clonal Expansion.Cells. 2020 Jan 31;9(2):331. doi: 10.3390/cells9020331. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32023857 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose enhances leptin signaling through modulation of AMPK activity.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e31636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0031636. Epub 2012 Feb 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22359610 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocytokines in thyroid dysfunction.ISRN Inflamm. 2013 Jun 23;2013:646271. doi: 10.1155/2013/646271. ISRN Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 24049662 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang, Y., Proenca, R., Maffei, M., Barone, M., Leopold, L., and Friedman, J. M. (1994) Nature 372 425–432 - PubMed
-
- Chen, H., Charlat, O., Tartaglia, L. A., Woolf, E. A., Weng, X., Ellis, S. J., Lakey, N. D., Culpepper, J., Moore, K. J., Breitbart, R. E., Duyk, G. M., Tepper, R. I., and Morgenstern, J. P. (1996) Cell 84 491–495 - PubMed
-
- Chua, S. C., Jr., Chung, W. K., Wu-Peng, X. S., Zhang, Y., Liu, S. M., Tartaglia, L., and Leibel, R. L. (1996) Science 271 994–996 - PubMed
-
- Lee, G. H., Proenca, R., Montez, J. M., Carroll, K. M., Darvishzadeh, J. G., Lee, J. I., and Friedman, J. M. (1996) Nature 379 632–635 - PubMed
-
- Vaisse, C., Halaas, J. L., Horvath, C. M., Darnell, J. E., Jr., Stoffel, M., and Friedman, J. M. (1996) Nat. Genet. 14 95–97 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

