Effects of L-lactate and D-mannitol on gamma-hydroxybutyrate toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics in rats
- PMID: 18719239
- PMCID: PMC2593404
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.108.022996
Effects of L-lactate and D-mannitol on gamma-hydroxybutyrate toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics in rats
Abstract
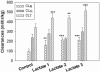
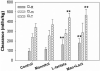
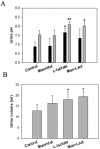
Overdoses of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), a drug of abuse, result in coma, respiratory arrest, and death. The objective of this study was to evaluate a potential GHB detoxification strategy by inhibiting the monocarboxylate transporter (MCT)-mediated renal reabsorption of GHB in rats, using the MCT substrate L-lactate. The use of the osmotic diuretic D-mannitol alone or combined with L-lactate was also explored. GHB (208 mg/h/kg) was infused i.v. for 3 h in the absence or presence of L-lactate (60.5, 121, and 302.5 mg h(-1) kg(-1)), D-mannitol (0.5 g/kg), or L-lactate (60.5 mg h(-1) kg(-1)) combined with D-mannitol (0.5 g/kg). GHB in plasma and urine samples was determined along with blood pH, electrolytes, glucose, and L-lactate. Administration of L-lactate, or the combination of L-lactate and D-mannitol, but not D-mannitol alone, significantly increased the renal and total clearances of GHB in rats. Blood pH and electrolyte concentrations exhibited small changes with GHB, GHB/lactate, and GHB/mannitol treatments, although most values remained within their normal range. The concomitant administration of lactated Ringer's solution (28 mM L-lactate) at 300 mul/min with mannitol (0.5 g/kg) resulted in a significant increase in GHB clearance and a decrease in sleep time after an i.v. dose of 1 g/kg. Overall, our results indicated the following: 1) the use of the MCT inhibitor L-lactate can increase the renal and total clearances of GHB, and 2) the combination of lactated Ringer's solution and D-mannitol significantly alters GHB toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics and represents a potential clinical detoxification strategy for the treatment of GHB overdoses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of monocarboxylate transporter inhibition on the oral toxicokinetics/toxicodynamics of γ-hydroxybutyrate and γ-butyrolactone.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Apr;345(1):102-10. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.202796. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23392755 Free PMC article.
-
Brain extracellular γ-hydroxybutyrate concentrations are decreased by L-lactate in rats: role in the treatment of overdoses.Pharm Res. 2013 May;30(5):1338-48. doi: 10.1007/s11095-013-0973-z. Epub 2013 Jan 15. Pharm Res. 2013. PMID: 23319173 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic modeling of monocarboxylate transporter-mediated toxicokinetic/toxicodynamic interactions between γ-hydroxybutyrate and L-lactate.AAPS J. 2014 Jul;16(4):756-70. doi: 10.1208/s12248-014-9593-8. Epub 2014 May 23. AAPS J. 2014. PMID: 24854892 Free PMC article.
-
γ-Hydroxybutyric Acid: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Toxicology.AAPS J. 2021 Jan 8;23(1):22. doi: 10.1208/s12248-020-00543-z. AAPS J. 2021. PMID: 33417072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interpreting γ-hydroxybutyrate concentrations for clinical and forensic purposes.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019 Mar;57(3):149-163. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2018.1519194. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019. PMID: 30307336 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on the toxicokinetics and sedative effects of the drug of abuse, γ-hydroxybutyric acid.J Pharm Sci. 2014 Oct;103(10):3310-5. doi: 10.1002/jps.24122. Epub 2014 Aug 29. J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 25174723 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of monocarboxylate transporter inhibition on the oral toxicokinetics/toxicodynamics of γ-hydroxybutyrate and γ-butyrolactone.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013 Apr;345(1):102-10. doi: 10.1124/jpet.112.202796. Epub 2013 Feb 7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2013. PMID: 23392755 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a local sensitivity analysis to inform study design based on a mechanistic toxicokinetic model for γ-hydroxybutyric acid.AAPS J. 2011 Jun;13(2):240-54. doi: 10.1208/s12248-011-9264-y. Epub 2011 Mar 9. AAPS J. 2011. PMID: 21387146 Free PMC article.
-
Concentration-effect relationships for the drug of abuse gamma-hydroxybutyric acid.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Jun;333(3):764-71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.109.165381. Epub 2010 Mar 9. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20215411 Free PMC article.
-
The Drug of Abuse Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid Exhibits Tissue-Specific Nonlinear Distribution.AAPS J. 2017 Dec 26;20(1):21. doi: 10.1208/s12248-017-0180-7. AAPS J. 2017. PMID: 29280004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andriamampandry C, Taleb O, Viry S, Muller C, Humbert JP, Gobaille S, Aunis D, Maitre M. Cloning and characterization of a rat brain receptor that binds the endogenous neuromodulator gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) FASEB J. 2003;17:1691–1693. - PubMed
-
- Arena C, Fung HL. Absorption of sodium gamma-hydroxybutyrate and its prodrug gamma-butyrolactone: relationship between in vitro transport and in vivo absorption. J Pharm Sci. 1980;69:356–358. - PubMed
-
- Benavides J, Rumigny JF, Bourguignon JJ, Wermuth CG, Mandel P, Maitre M. A high-affinity, Na+-dependent uptake system for gamma-hydroxybutyrate in membrane vesicles prepared from rat brain. J Neurochem. 1982;38:1570–1575. - PubMed
-
- Bernasconi R, Lauber J, Marescaux C, Vergnes M, Martin P, Rubio V, Leonhardt T, Reymann N, Bittiger H. Experimental absence seizures: potential role of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid and GABAB receptors. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1992;35:155–177. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya I, Boje KM. GHB (gamma-hydroxybutyrate) carrier-mediated transport across the blood-brain barrier. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004;311:92–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

