Aberrant expression of the hematopoietic-restricted minor histocompatibility antigen LRH-1 on solid tumors results in efficient cytotoxic T cell-mediated lysis
- PMID: 18719914
- PMCID: PMC11030113
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-008-0569-3
Aberrant expression of the hematopoietic-restricted minor histocompatibility antigen LRH-1 on solid tumors results in efficient cytotoxic T cell-mediated lysis
Abstract
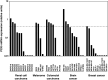
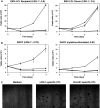
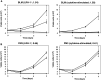
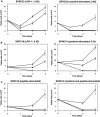
CD8(+) T cells recognizing minor histocompatibility antigens (MiHA) on solid tumor cells may mediate effective graft-versus-tumor (GVT) reactivity after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT). Previously, we identified LRH-1 as a hematopoietic-restricted MiHA encoded by the P2X5 gene. Here, we report that LRH-1 is aberrantly expressed on solid tumor cells. P2X5 mRNA expression is demonstrated in a significant portion of solid tumor cell lines, including renal cell carcinoma (RCC), melanoma, colorectal carcinoma, brain cancer and breast cancer. Importantly, P2X5 gene expression was also detected in a subset of primary solid tumor specimens derived from RCC, brain cancer and breast cancer patients. Furthermore, P2X5 expressing solid tumor cells can be effectively targeted by LRH-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes under inflammatory conditions. The expression of HLA-B7 and CD54 on tumor cells increases upon cytokine stimulation resulting in improved T cell activation as observed by higher levels of degranulation and enhanced tumor cell lysis. Overall, hematopoietic-restricted MiHA LRH-1 is aberrantly expressed on solid tumor cells and may be used as target in GVT-specific immunotherapy after SCT.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficient activation of LRH-1-specific CD8+ T-cell responses from transplanted leukemia patients by stimulation with P2X5 mRNA-electroporated dendritic cells.J Immunother. 2009 Jul-Aug;32(6):539-51. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181987c22. J Immunother. 2009. PMID: 19483655
-
A frameshift polymorphism in P2X5 elicits an allogeneic cytotoxic T lymphocyte response associated with remission of chronic myeloid leukemia.J Clin Invest. 2005 Dec;115(12):3506-16. doi: 10.1172/JCI24832. J Clin Invest. 2005. PMID: 16322791 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of P2X5 in lymphoid malignancies results in LRH-1-specific cytotoxic T-cell-mediated lysis.Br J Haematol. 2008 Jun;141(6):799-807. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07125.x. Epub 2008 Apr 10. Br J Haematol. 2008. PMID: 18410452
-
Minor histocompatibility antigens: allo target molecules for tumor-specific immunotherapy.Cancer J. 2004 Jan-Feb;10(1):1-7. doi: 10.1097/00130404-200401000-00001. Cancer J. 2004. PMID: 15000488 Review.
-
Strategies for the identification of T cell-recognized tumor antigens in hematological malignancies for improved graft-versus-tumor responses after allogeneic blood and marrow transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015 Jun;21(6):1000-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015. PMID: 25459643 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
P2 purinergic receptors regulate the progression of colorectal cancer.Purinergic Signal. 2023 Dec 28. doi: 10.1007/s11302-023-09983-6. Online ahead of print. Purinergic Signal. 2023. PMID: 38153612 Review.
-
A polymorphism in the splice donor site of ZNF419 results in the novel renal cell carcinoma-associated minor histocompatibility antigen ZAPHIR.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21699. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021699. Epub 2011 Jun 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21738768 Free PMC article.
-
Susceptibility Genes and Chromosomal Regions Associated With Non-Syndromic Familial Non-Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: Some Pathogenetic and Diagnostic Keys.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 28;13:829103. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.829103. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35295987 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for renal cell carcinoma: ten years after.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011 Jun;11(6):763-73. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2011.566855. Epub 2011 Mar 21. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011. PMID: 21417772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Durable remission of renal cell carcinoma in conjuncture with graft versus host disease following allogeneic stem cell transplantation and donor lymphocyte infusion: rule or exception?PLoS One. 2014 Jan 15;9(1):e85198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085198. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24454818 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bregni M, Dodero A, Peccatori J, Pescarollo A, Bernardi M, Sassi I, Voena C, Zaniboni A, Bordignon C, Corradini P. Nonmyeloablative conditioning followed by hematopoietic cell allografting and donor lymphocyte infusions for patients with metastatic renal and breast cancer. Blood. 2002;99(11):4234–4236. doi: 10.1182/blood.V99.11.4234. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

