Development and evaluation of lorazepam microemulsions for parenteral delivery
- PMID: 18720016
- PMCID: PMC2977031
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-008-9131-z
Development and evaluation of lorazepam microemulsions for parenteral delivery
Abstract
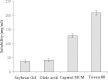
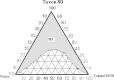
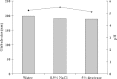
The objective of this investigation was to develop lorazepam (LZM) microemulsions as an alternative to the conventional cosolvent based formulation. Solubility of LZM in various oils and Tween 80 was determined. The ternary diagram was plotted to identify area of microemulsion existence and a suitable composition was identified to achieve desired LZM concentration. The LZM microemulsions were evaluated for compatibility with parenteral fluids, globule size, in vitro hemolysis and stability of LZM. Capmul MCM demonstrated highest solubilizing potential for LZM and was used as an oily phase. LZM microemulsions were compatible with parenteral dilution fluids and exhibited mean globule size less than 200 nm. The in vitro hemolysis studies indicated that microemulsions were well tolerated by erythrocytes. The LZM microemulsions containing amino acids exhibited good physical and chemical stability when subjected to refrigeration for 6 months.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources