Sickle red cell-endothelium interactions
- PMID: 18720225
- PMCID: PMC3059190
- DOI: 10.1080/10739680802279394
Sickle red cell-endothelium interactions
Abstract
Periodic recurrence of painful vaso-occlusive crisis is the defining feature of sickle cell disease. Among multiple pathologies associated with this disease, sickle red cell-endothelium interaction has been implicated as a potential initiating mechanism in vaso-occlusive events. This review focuses on various interrelated mechanisms involved in human sickle red cell adhesion. We discuss in vitro and microcirculatory findings on sickle red cell adhesion, its potential role in vaso-occlusion, and the current understanding of receptor-ligand interactions involved in this pathological phenomenon. In addition, we discuss the contribution of other cellular interactions (leukocytes recruitment and leukocyte-red cell interaction) to vaso-occlusion, as observed in transgenic sickle mouse models. Emphasis is given to recently discovered adhesion molecules that play a predominant role in mediating human sickle red cell adhesion. Finally, we analyze various therapeutic approaches for inhibiting sickle red cell adhesion by targeting adhesion molecules and also consider therapeutic strategies that target stimuli involved in endothelial activation and initiation of adhesion.
Figures
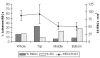


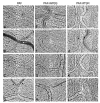

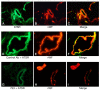

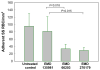
References
-
- Ballas SK, Larner J, Smith ED, Surrey S, Schwartz E, Rappaport EF. Rheologic predictors of the severity of the painful sickle cell crisis. Blood. 1988;72:1216–1223. - PubMed
-
- Barabino GA, Liu XD, Ewenstein BM, Kaul DK. Anionic polysaccharides inhibit adhesion of sickle erythrocytes to the vascular endothelium and result in improved hemodynamic behavior. Blood. 1999;93:1422–1429. - PubMed
-
- Barabino GA, McIntire LV, Eskin SG, Sears DA, Udden M. Endothelial cell interactions with sickle cell, sickle trait, mechanically injured, and normal erythrocytes under controlled flow. Blood. 1987;70:152–157. - PubMed
-
- Barabino GA, McIntire LV, Eskin SG, Sears DA, Udden M. Rheological studies of erythrocyte-endothelial cell interactions in sickle cell disease. Progress in Clinical & Biological Research. 1987;240:113–127. - PubMed
-
- Billett HH, Kim K, Fabry ME, Nagel RL. The percentage of dense red cells does not predict incidence of sickle cell painful crisis. Blood. 1986;68:301–303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

