Dopamine receptors in human lymphocytes: radioligand binding and quantitative RT-PCR assays
- PMID: 18721826
- PMCID: PMC2637390
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2008.07.018
Dopamine receptors in human lymphocytes: radioligand binding and quantitative RT-PCR assays
Abstract
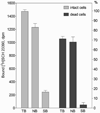
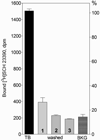
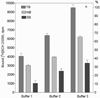
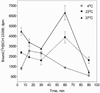
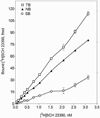
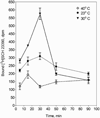
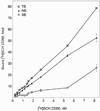
Analysis of dopamine receptors (DR) in lymphocytes of the human peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) fraction is an attractive tool for evaluation of functional properties of dopaminergic function underlying variation in complex psychological/psychopathological traits. Receptor binding assays (RBAs) with selective radioligands, which are widely used in CNS studies, have not produced consistent results when applied to isolated PBMC. We tested the assay conditions that could be essential for detection of DR in human PBMC and their membrane preparations. Using [(3)H]SCH23390, a dopamine D1-like receptor antagonist, we demonstrated the presence of two binding sites in PBMC-derived membrane fraction. One of them is characterized by the K(d) value consistent with that reported for D5 dopamine receptors in human lymphocytes, whereas the other K(d) value possibly corresponds to serotonin receptor(s). Although D5 receptor binding sites in PBMC membranes could be characterized by binding assays, the low protein expression and the large volume of blood needed for membrane preparation render the binding method impracticable for individual phenotyping. In contrast, real-time RT-PCR may be used for this purpose, contingent on the relationship between DR expression in the brain and in lymphocytes. The expression of the DRD2-DRD5 genes, as detected by this method, varied widely among samples, whereas the DRD1 expression was not detected. The expression levels were comparable with those in the brain for DRD3 and DRD4, and were significantly lower for DRD2 and DRD5.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low resilience to stress is associated with candidate gene expression alterations in the dopaminergic signalling pathway.Psychogeriatrics. 2018 May;18(3):190-201. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12312. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Psychogeriatrics. 2018. PMID: 29423959
-
Dopamine D2-like receptors on human peripheral blood lymphocytes: a radioligand binding assay and immunocytochemical study.J Auton Pharmacol. 1999 Jun;19(3):151-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2680.1999.00135.x. J Auton Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10511471
-
Dopamine receptor gene (DRD1-DRD5) expression changes as stress factors associated with breast cancer.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(23):10339-43. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.23.10339. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25556472
-
The peripheral dopaminergic system: morphological analysis, functional and clinical applications.Ital J Anat Embryol. 2002 Jul-Sep;107(3):145-67. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2002. PMID: 12437142 Review.
-
A comprehensive method for the quantitative determination of dopamine receptor subtypes.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;430:77-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb14499.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984. PMID: 6331265 Review.
Cited by
-
The mRNA Expression Status of Dopamine Receptor D2, Dopamine Receptor D3 and DARPP-32 in T Lymphocytes of Patients with Early Psychosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 6;16(11):26677-86. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125983. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26561806 Free PMC article.
-
Effect on the expression of drd2 and drd3 after neonatal lesion in the lymphocytes, nucleus accumbens, hippocampus and prefrontal cortex: comparative analysis between juvenile and adult Wistar rats.Hereditas. 2016 Nov 22;153:13. doi: 10.1186/s41065-016-0018-9. eCollection 2016. Hereditas. 2016. PMID: 28096775 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine, Immunity, and Disease.Pharmacol Rev. 2023 Jan;75(1):62-158. doi: 10.1124/pharmrev.122.000618. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Pharmacol Rev. 2023. PMID: 36757901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging role of dopamine in neovascularization of pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma.FASEB J. 2017 Jun;31(6):2226-2240. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601131R. Epub 2017 Mar 6. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28264974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential diagnostic markers of olanzapine efficiency for acute psychosis: a focus on peripheral biogenic amines.BMC Psychiatry. 2017 Dec 8;17(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1562-1. BMC Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 29221470 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Amenta F, Bronzetti E, Felici L, Ricci A, Tayebati SK. Dopamine D2-like receptors on human peripheral blood lymphocytes: a radioligand binding assay and immunocytochemical study. J Auton Pharmacol. 1999;19:151–159. - PubMed
-
- Aune TM, McGrath KM, Sarr T, Bombara MP, Kelley KA. Expression of 5HT1a receptors on activated human T cells. Regulation of cyclic AMP levels and T cell proliferation by 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Immunol. 1993;151:1175–1183. - PubMed
-
- Barbanti P, Fabbrini G, Ricci A, Bruno G, Cerbo R, Bronzetti E, Amenta F, Luigi Lenzi G. Reduced density of dopamine D2-like receptors on peripheral blood lymphocytes in Alzheimer's disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 2000a;120:65–75. - PubMed
-
- Barbanti P, Fabbrini G, Ricci A, Cerbo R, Bronzetti E, Caronti B, Calderaro C, Felici L, Stocchi F, Meco G, et al. Increased expression of dopamine receptors on lymphocytes in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 1999;14:764–771. - PubMed
-
- Barbanti P, Fabbrini G, Ricci A, Pascali MP, Bronzetti E, Amenta F, Lenzi GL, Cerbo R. Migraine patients show an increased density of dopamine D3 and D4 receptors on lymphocytes. Cephalalgia. 2000b;20:15–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

