Release of a model protein from biodegradable self assembled films for surface delivery applications
- PMID: 18721835
- PMCID: PMC2754560
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2008.07.032
Release of a model protein from biodegradable self assembled films for surface delivery applications
Abstract
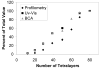
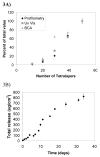
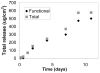
Layer-by-layer (LbL) films have multiple features that make them attractive for drug delivery, including the potential to sequentially deliver growth factors from implantable medical devices or tissue engineering scaffolds. To date, however, characterization has been lacking for protein delivery from such films. Here, LbL polyelectrolyte films constructed with the model protein lysozyme and a hydrolytically degradable and biocompatible synthetic polycation are characterized. Milligram/cm(2) scale linear or power law release profiles can be achieved over 2 to 34 days, and control over loading and release are demonstrated through parameters such as tuning the degradability of the synthetic polycation, changing the number of layers used, or changing the polysaccharide polyanion. Functionality is maintained at nearly 100%, underscoring mild processing conditions apt to preserve fragile protein function. LbL films thus have promise as a tool for exploring protein modulation of the interaction between implanted surfaces and the cells they contact.
Figures


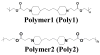
Similar articles
-
Multilayer films assembled from naturally-derived materials for controlled protein release.Biomacromolecules. 2014 Jun 9;15(6):2049-57. doi: 10.1021/bm5001839. Epub 2014 May 30. Biomacromolecules. 2014. PMID: 24825478 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained protein release from hydrogel microparticles using layer-by-layer (LbL) technology.Drug Deliv. 2016 Oct;23(8):2747-2755. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2015.1069422. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Drug Deliv. 2016. PMID: 26289209
-
Tailoring the chain packing in ultrathin polyelectrolyte films formed by sequential adsorption: nanoscale probing by positron annihilation spectroscopy.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 Dec 5;134(48):19808-19. doi: 10.1021/ja308716v. Epub 2012 Nov 21. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 23170945
-
Biomedical applications of electrostatic layer-by-layer nano-assembly of polymers, enzymes, and nanoparticles.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2003;39(1):23-43. doi: 10.1385/CBB:39:1:23. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2003. PMID: 12835527 Review.
-
Modulating the release kinetics through the control of the permeability of the layer-by-layer assembly: a review.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009 Jun;6(6):585-97. doi: 10.1517/17425240902967599. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009. PMID: 19480609 Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue integration of growth factor-eluting layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte multilayer coated implants.Biomaterials. 2011 Feb;32(5):1446-53. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.052. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Biomaterials. 2011. PMID: 21084117 Free PMC article.
-
Shifts in macrophage phenotype at the biomaterial interface via IL-4 eluting coatings are associated with improved implant integration.Biomaterials. 2017 Jan;112:95-107. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.019. Epub 2016 Oct 11. Biomaterials. 2017. PMID: 27760399 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembled Biodegradable Nanoparticles and Polysaccharides as Biomimetic ECM Nanostructures for the Synergistic effect of RGD and BMP-2 on Bone Formation.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 28;6:25090. doi: 10.1038/srep25090. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27121121 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro behavior of layer-by-layer deposited molecular oligoelectrolyte films on Ti-6Al-4V surfaces.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009 Dec;20(12):2455-63. doi: 10.1007/s10856-009-3825-y. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009. PMID: 19634005
-
Synthetic Charge-Invertible Polymer for Rapid and Complete Implantation of Layer-by-Layer Microneedle Drug Films for Enhanced Transdermal Vaccination.ACS Nano. 2018 Oct 23;12(10):10272-10280. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05373. Epub 2018 Oct 4. ACS Nano. 2018. PMID: 30272942 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Decher G. Fuzzy nanoassemblies: Toward layered polymeric multicomposites. Science. 1997;277(5330):1232–1237.
-
- Vazquez E, Dewitt DM, Hammond PT, Lynn DM. Construction of hydrolytically-degradable thin films via layer-by-layer deposition of degradable polyelectrolytes. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 2002;124(47):13992–13993. - PubMed
-
- Decher G, Eckle M, Schmitt J, Struth B. Layer-by-layer assembled multicomposite films. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science. 1998;3(1):32–39.
-
- Hammond PT. Form and function in multilayer assembly: New applications at the nanoscale. Advanced Materials. 2004;16(15):1271–1293.
-
- Fu K, Pack DW, Klibanov AM, Langer R. Visual evidence of acidic environment within degrading poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) microspheres. Pharmaceutical Research. 2000;17(1):100–106. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

