Toll-like receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus; prospects for therapeutic intervention
- PMID: 18722558
- PMCID: PMC2654252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.autrev.2008.07.046
Toll-like receptors in systemic lupus erythematosus; prospects for therapeutic intervention
Abstract
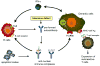
Recent experimental and clinical studies have placed new emphasis on the role of the innate immune system in SLE. Nucleic acid-containing immune complexes activate the innate response by engaging specific Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and promote the generation of autoantibodies. Pharmacologic modulation of TLR-directed pathways may offer new therapeutic approaches for the treatment of SLE.
Figures
References
-
- Takeda K, Kaisho T, Akira S. Toll-like receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:335–376. - PubMed
-
- Baccala R, Hoebe K, Kono DH, Beutler B, Theofilopoulos AN. TLR-dependent and TLR-independent pathways of type I interferon induction in systemic autoimmunity. Nat Med. 2007;13:543–551. - PubMed
-
- Sano H, Morimoto C. Dna isolated from DNA/anti-DNA antibody immune complexes in systemic lupus erythematosus is rich in guanine-cytosine content. J Immunol. 1982;128:1341–1345. - PubMed
-
- Isenberg DA, Ehrenstein MR, Longhurst C, Kalsi JK. The origin, sequence, structure, and consequences of developing anti-DNA antibodies. A human perspective. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:169–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

