Treatment with an Interleukin 1 beta antibody improves glycemic control in diet-induced obesity
- PMID: 18723371
- PMCID: PMC3063393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2008.07.004
Treatment with an Interleukin 1 beta antibody improves glycemic control in diet-induced obesity
Abstract
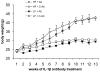
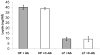
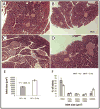
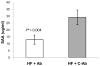
The proinflammatory cytokine Interleukin 1 beta (IL-1beta) is elevated in obese individuals and rodents and it is implicated in impaired insulin secretion, decreased cell proliferation and apoptosis of pancreatic beta cells. In this study we describe the therapeutic effects by an IL-1beta antibody to improve glucose control in hyperglycemic mice with diet-induced obesity. After 13 weeks of treatment the IL-1beta antibody treated group showed reduced glycated hemoglobin (( *)P=0.049), reduced serum levels of proinsulin (( *)P=0.015), reduced levels of insulin and smaller islet size (( *)P=1.65E-13) relative to the control antibody treated group. Neutralization of IL-1beta also significantly reduced serum amyloid A (SAA) which is an indicator of inflammation-induced acute phase response (( *)P=0.024). While there was no improvement of obesity, a significant improvement of glycemic control and of beta cell function is achieved by this pharmacological treatment which may slow/prevent disease progression in Type 2 Diabetes.
Figures

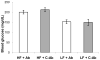


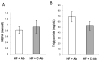
References
-
- Vincent RP, le Roux CW. New agents in development for the management of obesity. Int J Clin Pract 2007 - PubMed
-
- Yudkin JS, Stehouwer CD, Emeis JJ, Coppack SW. C-reactive protein in healthy subjects: associations with obesity, insulin resistance, and endothelial dysfunction: a potential role for cytokines originating from adipose tissue? Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19:972–978. - PubMed
-
- Festa A, D’Agostino R, Jr, Williams K, Karter AJ, Mayer-Davis EJ, Tracy RP, Haffner SM. The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2001;25:1407–1415. - PubMed
-
- Engstrom G, Hedblad B, Stavenow L, Lind P, Janzon L, Lindgarde F. Inflammation-sensitive plasma proteins are associated with future weight gain. Diabetes. 2003;52:2097–2101. - PubMed
-
- Dandona P, Aljada A. A rational approach to pathogenesis and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 2002;90:27G–33G. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

