Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis
- PMID: 18723672
- PMCID: PMC2529064
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805038105
Dysregulation of microRNAs after myocardial infarction reveals a role of miR-29 in cardiac fibrosis
Abstract
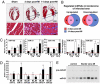
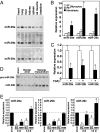
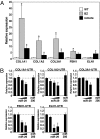
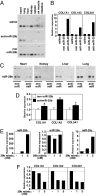
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) due to coronary artery occlusion is accompanied by a pathological remodeling response that includes hypertrophic cardiac growth and fibrosis, which impair cardiac contractility. Previously, we showed that cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure are accompanied by characteristic changes in the expression of a collection of specific microRNAs (miRNAs), which act as negative regulators of gene expression. Here, we show that MI in mice and humans also results in the dysregulation of specific miRNAs, which are similar to but distinct from those involved in hypertrophy and heart failure. Among the MI-regulated miRNAs are members of the miR-29 family, which are down-regulated in the region of the heart adjacent to the infarct. The miR-29 family targets a cadre of mRNAs that encode proteins involved in fibrosis, including multiple collagens, fibrillins, and elastin. Thus, down-regulation of miR-29 would be predicted to derepress the expression of these mRNAs and enhance the fibrotic response. Indeed, down-regulation of miR-29 with anti-miRs in vitro and in vivo induces the expression of collagens, whereas over-expression of miR-29 in fibroblasts reduces collagen expression. We conclude that miR-29 acts as a regulator of cardiac fibrosis and represents a potential therapeutic target for tissue fibrosis in general.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: E.v.R., W.S.M., and E.N.O. are cofounders of MiRagen Therapeutics.
Figures
References
-
- Fox CS, et al. Increasing cardiovascular disease burden due to diabetes mellitus: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation. 2007;115:1544–1550. - PubMed
-
- Swynghedauw B. Molecular mechanisms of myocardial remodeling. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:215–262. - PubMed
-
- Bouzeghrane F, Reinhardt DP, Reudelhuber TL, Thibault G. Enhanced expression of fibrillin-1, a constituent of the myocardial extracellular matrix in fibrosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;289:H982–991. - PubMed
-
- Powell DW, et al. Myofibroblasts. I. Paracrine cells important in health and disease. Am J Physiol. 1999;277:C1–C9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

