Lack of adrenomedullin in the mouse brain results in behavioral changes, anxiety, and lower survival under stress conditions
- PMID: 18723674
- PMCID: PMC2527954
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0803174105
Lack of adrenomedullin in the mouse brain results in behavioral changes, anxiety, and lower survival under stress conditions
Abstract
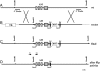
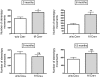
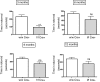
The adrenomedullin (AM) gene, adm, is widely expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) and several functions have been suggested for brain AM. Until now, a formal confirmation of these actions using genetic models has been elusive since the systemic adm knockout results in embryo lethality. We have built a conditional knockout mouse model using the Cre/loxP approach. When crossed with transgenic mice expressing the Cre recombinase under the tubulin Talpha-1 promoter, we obtained animals with no AM expression in the CNS but normal levels in other organs. These animals lead normal lives and do not present any gross morphological defect. Specific areas of the brain of animals lacking CNS AM contain hyperpolymerized tubulin, a consequence of AM downregulation. Behavioral analysis shows that mice with no AM in their brain have impaired motor coordination and are hyperactive and overanxious when compared to their wild-type littermates. Treatment with methylphenidate, haloperidol, and diazepam did not show differences between genotypes. Circulating levels of adrenocorticotropic hormone and corticosterone were similar in knockout and wild-type mice. Animals with no brain AM were less resistant to hypobaric hypoxia than wild-type mice, demonstrating the neuroprotective function of AM in the CNS. In conclusion, AM exerts a beneficial action in the brain by maintaining homeostasis both under normal and stress conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


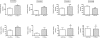
References
-
- Lopez J, Martinez A. Cell and molecular biology of the multifunctional peptide, adrenomedullin. Int Rev Cytol. 2002;221:1–92. - PubMed
-
- McLatchie LM, et al. RAMPs regulate the transport and ligand specificity of the calcitonin-receptor-like receptor. Nature. 1998;393:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Ueta Y, et al. Adrenomedullin-immunoreactive neurons in the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1995;202:37–40. - PubMed
-
- Serrano J, et al. Distribution of adrenomedullin-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system by light and electron microscopy. Brain Res. 2000;853:245–268. - PubMed
-
- Ueda T, Ugawa S, Saishin Y, Shimada S. Expression of receptor-activity modifying protein (RAMP) mRNAs in the mouse brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2001;93:36–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

