Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 enhances alpha1D-adrenergic receptor constriction
- PMID: 18723764
- PMCID: PMC2593515
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00564.2008
Inhibition of vascular smooth muscle G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 enhances alpha1D-adrenergic receptor constriction
Abstract
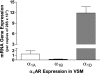
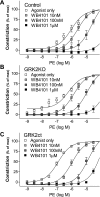
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) is a serine/theorinine kinase that phosphorylates and desensitizes agonist-bound G protein-coupled receptors. GRK2 is increased in expression and activity in lymphocytes and vascular smooth muscle (VSM) in human hypertension and animal models of the disease. Inhibition of GRK2 using the carboxyl-terminal portion of the protein (GRK2ct) has been an effective tool to restore compromised beta-adrenergic receptor (AR) function in heart failure and improve outcome. A well-characterized dysfunction in hypertension is attenuation of betaAR-mediated vasodilation. Therefore, we tested the role of inhibition of GRK2 using GRK2ct or VSM-selective GRK2 gene ablation in a renal artery stenosis model of elevated blood pressure (BP) [the two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) model]. Use of the 2K1C model resulted in a 30% increase in conscious BP, a threefold increase in plasma norepinephrine levels, and a 50% increase in VSM GRK2 mRNA levels. BP remained increased despite VSM-specific GRK2 inhibition by either GRK2 knockout (GRK2KO) or peptide inhibition (GRK2ct). Although betaAR-mediated dilation in vivo and in situ was enhanced, alpha(1)AR-mediated vasoconstriction was also increased. Further pharmacological experiments using alpha(1)AR antagonists revealed that GRK2 inhibition of expression (GRK2KO) or activity (GRK2ct) enhanced alpha(1D)AR vasoconstriction. This is the first study to suggest that VSM alpha(1D)ARs are a GRK2 substrate in vivo.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Erythropoietin Reverses Sepsis-Induced Vasoplegia to Norepinephrine Through Preservation of α1D-Adrenoceptor mRNA Expression and Inhibition of GRK2-Mediated Desensitization in Mouse Aorta.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Jan;21(1):100-13. doi: 10.1177/1074248415587968. Epub 2015 May 28. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26025460
-
Vascular-targeted overexpression of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-2 in transgenic mice attenuates beta-adrenergic receptor signaling and increases resting blood pressure.Mol Pharmacol. 2002 Apr;61(4):749-58. doi: 10.1124/mol.61.4.749. Mol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11901213
-
Gβγ-independent recruitment of G-protein coupled receptor kinase 2 drives tumor necrosis factor α-induced cardiac β-adrenergic receptor dysfunction.Circulation. 2013 Jul 23;128(4):377-87. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.003183. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Circulation. 2013. PMID: 23785004 Free PMC article.
-
GRK2 inhibition in heart failure: something old, something new.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(2):186-91. doi: 10.2174/138161212799040510. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22229578 Review.
-
Canonical or non-canonical, all aspects of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 in heart failure.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025 Mar;241(3):e70010. doi: 10.1111/apha.70010. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2025. PMID: 39960030 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The complex G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) interactome unveils new physiopathological targets.Br J Pharmacol. 2010 Jun;160(4):821-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00727.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20590581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 and arrestin2 regulate arterial smooth muscle P2Y-purinoceptor signalling.Cardiovasc Res. 2011 Jan 1;89(1):193-203. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq249. Epub 2010 Aug 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2011. PMID: 20705669 Free PMC article.
-
G protein coupled receptor kinases as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease.Circ Res. 2011 Jul 22;109(3):309-19. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.231233. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21778435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GRK2 targeted knock-down results in spontaneous hypertension, and altered vascular GPCR signaling.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):5141-5155. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.615658. Epub 2015 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25561731 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled receptor kinases in hypertension: physiology, pathogenesis, and therapeutic targets.Hypertens Res. 2024 Sep;47(9):2317-2336. doi: 10.1038/s41440-024-01763-y. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Hypertens Res. 2024. PMID: 38961282 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chruscinski A, Brede ME, Meinel L, Lohse MJ, Kobilka BK, Hein L. Differential distribution of beta-adrenergic receptor subtypes in blood vessels of knockout mice lacking β1- or β2-adrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol 60: 955–962, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Corry DB, Tuck ML. Obesity, hypertension, and sympathetic nervous system activity. Curr Hypertens Rep 1: 119–126, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Daly CJ, Deighan C, McGee A, Mennie D, Ali Z, McBride M, McGrath JC. A knockout approach indicates a minor vasoconstrictor role for vascular α1B-adrenoceptors in mouse. Physiol Genomics 9: 85–91, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

