A sequence motif within chromatin entry sites directs MSL establishment on the Drosophila X chromosome
- PMID: 18724933
- PMCID: PMC2613042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.06.033
A sequence motif within chromatin entry sites directs MSL establishment on the Drosophila X chromosome
Abstract
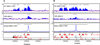
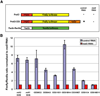
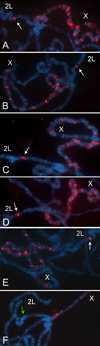
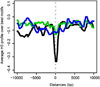
The Drosophila MSL complex associates with active genes specifically on the male X chromosome to acetylate histone H4 at lysine 16 and increase expression approximately 2-fold. To date, no DNA sequence has been discovered to explain the specificity of MSL binding. We hypothesized that sequence-specific targeting occurs at "chromatin entry sites," but the majority of sites are sequence independent. Here we characterize 150 potential entry sites by ChIP-chip and ChIP-seq and discover a GA-rich MSL recognition element (MRE). The motif is only slightly enriched on the X chromosome ( approximately 2-fold), but this is doubled when considering its preferential location within or 3' to active genes (>4-fold enrichment). When inserted on an autosome, a newly identified site can direct local MSL spreading to flanking active genes. These results provide strong evidence for both sequence-dependent and -independent steps in MSL targeting of dosage compensation to the male X chromosome.
Figures


References
-
- Amrein H, Axel R. Genes expressed in neurons of adult male Drosophila. Cell. 1997;88:459–469. - PubMed
-
- Bashaw GJ, Baker BS. The msl-2 dosage compensation gene of Drosophila encodes a putative DNA-binding protein whose expression is sex specifically regulated by Sex-lethal. Development. 1995;121:3245–3258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

