The RNAseIII enzyme Drosha is critical in T cells for preventing lethal inflammatory disease
- PMID: 18725527
- PMCID: PMC2526196
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20081219
The RNAseIII enzyme Drosha is critical in T cells for preventing lethal inflammatory disease
Erratum in
- J Exp Med. 2008 Sep 29;205(10). doi: 10.1084/jem.20071219090508c. Rundensky, Alexander Y [corrected to Rudensky, Alexander Y]
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are implicated in the differentiation and function of many cell types. We provide genetic and in vivo evidence that the two RNaseIII enzymes, Drosha and Dicer, do indeed function in the same pathway. These have previously been shown to mediate the stepwise maturation of miRNAs (Lee, Y., C. Ahn, J. Han, H. Choi, J. Kim, J. Yim, J. Lee, P. Provost, O. Radmark, S. Kim, and V.N. Kim. 2003. Nature. 425:415-419), and genetic ablation of either within the T cell compartment, or specifically within Foxp3(+) regulatory T (T reg) cells, results in identical phenotypes. We found that miRNA biogenesis is indispensable for the function of T reg cells. Specific deletion of either Drosha or Dicer phenocopies mice lacking a functional Foxp3 gene or Foxp3(+) cells, whereas deletion throughout the T cell compartment also results in spontaneous inflammatory disease, but later in life. Thus, miRNA-dependent regulation is critical for preventing spontaneous inflammation and autoimmunity.
Figures
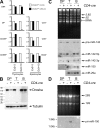




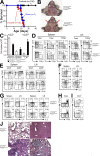
References
-
- Bennett, C.L., M.E. Brunkow, F. Ramsdell, K.C. O'Briant, Q. Zhu, R.L. Fuleihan, A.O. Shigeoka, H.D. Ochs, and P.F. Chance. 2001. A rare polyadenylation signal mutation of the FOXP3 gene (AAUAAA→AAUGAA) leads to the IPEX syndrome. Immunogenetics. 53:435–439. - PubMed
-
- Brunkow, M.E., E.W. Jeffery, K.A. Hjerrild, B. Paeper, L.B. Clark, S.A. Yasayko, J.E. Wilkinson, D. Galas, S.F. Ziegler, and F. Ramsdell. 2001. Disruption of a new forkhead/winged-helix protein, scurfin, results in the fatal lymphoproliferative disorder of the scurfy mouse. Nat. Genet. 27:68–73. - PubMed
-
- Kim, J.M., J.P. Rasmussen, and A.Y. Rudensky. 2007. Regulatory T cells prevent catastrophic autoimmunity throughout the lifespan of mice. Nat. Immunol. 8:191–197. - PubMed
-
- Wildin, R.S., F. Ramsdell, J. Peake, F. Faravelli, J.L. Casanova, N. Buist, E. Levy-Lahad, M. Mazzella, O. Goulet, L. Perroni, et al. 2001. X-linked neonatal diabetes mellitus, enteropathy and endocrinopathy syndrome is the human equivalent of mouse scurfy. Nat. Genet. 27:18–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

