A thermodynamic model for Nap1-histone interactions
- PMID: 18728017
- PMCID: PMC2583301
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M805918200
A thermodynamic model for Nap1-histone interactions
Abstract
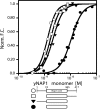
The yeast nucleosome assembly protein 1 (yNap1) plays a role in chromatin maintenance by facilitating histone exchange as well as nucleosome assembly and disassembly. It has been suggested that yNap1 carries out these functions by regulating the concentration of free histones. Therefore, a quantitative understanding of yNap1-histone interactions also provides information on the thermodynamics of chromatin. We have developed quantitative methods to study the affinity of yNap1 for histones. We show that yNap1 binds H2A/H2B and H3/H4 histone complexes with low nm affinity, and that each yNap1 dimer binds two histone fold dimers. The yNap1 tails contribute synergistically to histone binding while the histone tails have a slightly repressive effect on binding. The (H3/H4)(2) tetramer binds DNA with higher affinity than it binds yNap1.
Figures


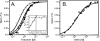

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

