Electron probe X-ray microanalysis of intact pathway for human aqueous humor outflow
- PMID: 18753314
- PMCID: PMC2584983
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.340.2008
Electron probe X-ray microanalysis of intact pathway for human aqueous humor outflow
Abstract
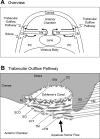
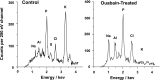
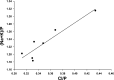
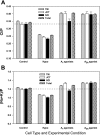
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is regulated by the resistance to outflow of the eye's aqueous humor. Elevated resistance raises IOP and can cause glaucoma. Despite the importance of outflow resistance, its site and regulation are unclear. The small size, complex geometry, and relative inaccessibility of the outflow pathway have limited study to whole animal, whole eye, or anterior-segment preparations, or isolated cells. We now report measuring elemental contents of the heterogeneous cell types within the intact human trabecular outflow pathway using electron-probe X-ray microanalysis. Baseline contents of Na(+), K(+), Cl(-), and P and volume (monitored as Na+K contents) were comparable to those of epithelial cells previously studied. Elemental contents and volume were altered by ouabain to block Na(+)-K(+)-activated ATPase and by hypotonicity to trigger a regulatory volume decrease (RVD). Previous results with isolated trabecular meshwork (TM) cells had disagreed whether TM cells express an RVD. In the intact tissue, we found that all cells, including TM cells, displayed a regulatory solute release consistent with an RVD. Selective agonists of A(1) and A(2) adenosine receptors (ARs), which exert opposite effects on IOP, produced similar effects on juxtacanalicular (JCT) cells, previously inaccessible to functional study, but not on Schlemm's canal cells that adjoin the JCT. The results obtained with hypotonicity and AR agonists indicate the potential of this approach to dissect physiological mechanisms in an area that is extremely difficult to study functionally and demonstrate the utility of electron microprobe analysis in studying the cellular physiology of the human trabecular outflow pathway in situ.
Figures


References
-
- Abraham EH, Breslow JL, Epstein J, Chang-Sing P, Lechene C. Preparation of individual human diploid fibroblasts and study of ion transport. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 248: C154–C164, 1985. - PubMed
-
- Al-Aswad LA, Gong H, Lee D, O'Donnell ME, Brandt JD, Ryan WJ, Schroeder A, Erickson KA. Effects of Na-K-2Cl cotransport regulators on outflow facility in calf and human eyes in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40: 1695–1701, 1999. - PubMed
-
- Avila MY, Carré DA, Stone RA, Civan MM. Reliable measurement of mouse intraocular pressure by a servo-null micropipette system. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 42: 1841–1846, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Avila MY, Seidler RW, Stone RA, Civan MM. Inhibitors of NHE-1 Na+/H+ exchange reduce mouse intraocular pressure. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43: 1897–1902, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

