Early mechanical dysfunction of the diaphragm in the muscular dystrophy with myositis (Ttnmdm) model
- PMID: 18753318
- PMCID: PMC2584999
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.16.2008
Early mechanical dysfunction of the diaphragm in the muscular dystrophy with myositis (Ttnmdm) model
Abstract
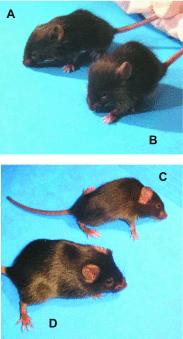
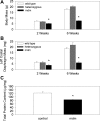
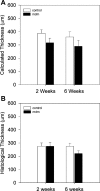
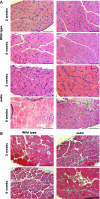
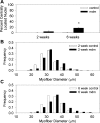
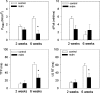
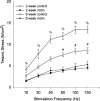
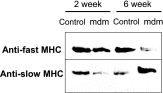
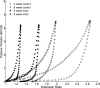
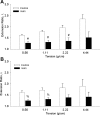
A complex rearrangement mutation in the mouse titin gene leads to an in-frame 83-amino acid deletion in the N2A region of titin. Autosomal recessive inheritance of the titin muscular dystrophy with myositis (Ttn(mdm/mdm)) mutation leads to a severe early-onset muscular dystrophy and premature death. We hypothesized that the N2A deletion would negatively impact the force-generating capacity and passive mechanical properties of the mdm diaphragm. We measured in vitro active isometric contractile and passive length-tension properties to assess muscle function at 2 and 6 wk of age. Micro-CT, myosin heavy chain Western blotting, and histology were used to assess diaphragm structure. Marked chest wall distortions began at 2 wk and progressively worsened until 5 wk. The percentage of myofibers with centrally located nuclei in mdm mice was significantly (P < 0.01) increased at 2 and 6 wk by 4% and 17%, respectively, compared with controls. At 6 wk, mdm diaphragm twitch stress was significantly (P < 0.01) reduced by 71%, time to peak twitch was significantly (P < 0.05) reduced by 52%, and half-relaxation time was significantly (P < 0.05) reduced by 57%. Isometric tetanic stress was significantly (P < 0.05) depressed in 2- and 6-wk mdm diaphragms by as much as 64%. Length-tension relationships of the 2- and 6-wk mdm diaphragms showed significantly (P < 0.05) decreased extensibility and increased stiffness. Slow myosin heavy chain expression was aberrantly favored in the mdm diaphragm at 6 wk. Our data strongly support early contractile and passive mechanical aberrations of the respiratory pump in mdm mice.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N2A Titin: Signaling Hub and Mechanical Switch in Skeletal Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 1;21(11):3974. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113974. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32492876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Induction and myofibrillar targeting of CARP, and suppression of the Nkx2.5 pathway in the MDM mouse with impaired titin-based signaling.J Mol Biol. 2004 Feb 6;336(1):145-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2003.12.021. J Mol Biol. 2004. PMID: 14741210
-
The muscular dystrophy with myositis (mdm) mouse mutation disrupts a skeletal muscle-specific domain of titin.Genomics. 2002 Feb;79(2):146-9. doi: 10.1006/geno.2002.6685. Genomics. 2002. PMID: 11829483
-
Mdm muscular dystrophy: interactions with calpain 3 and a novel functional role for titin's N2A domain.Hum Mol Genet. 2005 Oct 1;14(19):2801-11. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddi313. Epub 2005 Aug 22. Hum Mol Genet. 2005. PMID: 16115818 Free PMC article.
-
Diaphragm contractile weakness due to reduced mechanical loading: role of titin.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):C167-C176. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00509.2018. Epub 2019 May 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31042425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ANKRD1 expression is aberrantly upregulated in the mdm mouse model of muscular dystrophy and induced by stretch through NFκB.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2024 Dec;45(4):191-200. doi: 10.1007/s10974-024-09671-x. Epub 2024 Apr 29. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2024. PMID: 38683293
-
N2A Titin: Signaling Hub and Mechanical Switch in Skeletal Muscle.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 1;21(11):3974. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113974. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32492876 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of a skeletal muscle titin mutation on walking in mice.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2017 Jan;203(1):67-76. doi: 10.1007/s00359-016-1137-5. Epub 2016 Dec 16. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27986994
-
Anisotropic regulation of Ankrd2 gene expression in skeletal muscle by mechanical stretch.FASEB J. 2010 Sep;24(9):3330-40. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-158386. Epub 2010 May 4. FASEB J. 2010. PMID: 20442316 Free PMC article.
-
Contributions of Titin and Collagen to Passive Stress in Muscles from mdm Mice with a Small Deletion in Titin's Molecular Spring.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 9;23(16):8858. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168858. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boriek AM, Liu S, Rodarte JR. Costal diaphragm curvature in the dog. J Appl Physiol 75: 527–533, 1993. - PubMed
-
- Boriek AM, Rodarte JR, Reid MB. Shape and tension distribution of the passive rat diaphragm. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 280: R33–R41, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda N, Granzier HL, Ishiwata S, Kurihara S. Physiological functions of the giant elastic protein titin in mammalian striated muscle. J Physiol Sci 58: 151–159, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Garvey SM, Rajan C, Lerner AP, Frankel WN, Cox GA. The muscular dystrophy with myositis (mdm) mouse mutation disrupts a skeletal muscle-specific domain of titin. Genomics 79: 146–149, 2002. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

