Suppression of mutant Huntingtin aggregate formation by Cdk5/p35 through the effect on microtubule stability
- PMID: 18753376
- PMCID: PMC6670830
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0973-08.2008
Suppression of mutant Huntingtin aggregate formation by Cdk5/p35 through the effect on microtubule stability
Abstract
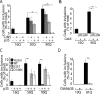
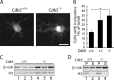
Huntington's disease (HD) is a polyglutamine [poly(Q)] disease with an expanded poly(Q) stretch in the N terminus of the huntingtin protein (htt). A major pathological feature of HD neurons is inclusion bodies, detergent-insoluble aggregates composed of poly(Q)-expanded mutant htt (mhtt). Misfolding of mhtt is thought to confer a toxic property via formation of aggregates. Although toxic molecular species are still debated, it is important to clarify the aggregation mechanism to understand the pathogenesis of mhtt. We show Cdk5/p35 suppresses the formation of mhtt inclusion bodies in cell lines and primary neurons. Although we expressed the N-terminal exon 1 fragment of htt lacking phosphorylation sites for Cdk5 in COS-7 cells, the kinase activity of Cdk5 was required for the suppression. Furthermore, Cdk5/p35 suppressed inclusion formation of atrophin-1, another poly(Q) protein, raising the possibility that Cdk5/p35 generally suppresses inclusion formation of poly(Q) proteins. Microtubules (MTs) were a downstream component of Cdk5/p35 in the suppression of inclusion formation; Cdk5/p35 disrupted MTs, which were required for the formation of inclusions. Moreover, stabilization of MTs by Taxol induced inclusions even with overexpression of Cdk5/p35. The formation of inclusions was also regulated by manipulating the Cdk5/p35 activity in primary rat or mouse cortical neuron cultures. These results indicate that Cdk5-dependent regulation of MT organization is involved in the development of aggregate formation and subsequent pathogenesis of poly(Q) diseases. This Cdk5 inhibition of htt aggregates is a novel mechanism different from htt phosphorylation and interaction with Cdk5 reported previously (Luo et al., 2005; Anne et al., 2007).
Figures




References
-
- Arrasate M, Mitra S, Schweitzer ES, Segal MR, Finkbeiner S. Inclusion body formation reduces levels of mutant huntingtin and the risk of neuronal death. Nature. 2004;431:805–810. - PubMed
-
- Bennett EJ, Shaler TA, Woodman B, Ryu KY, Zaitseva TS, Becker CH, Bates GP, Schulman H, Kopito RR. Global changes to the ubiquitin system in Huntington's disease. Nature. 2007;448:704–708. - PubMed
-
- Cattaneo E, Zuccato C, Tartari M. Normal huntingtin function: an alternative approach to Huntington's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:919–930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
