Determination of pyrophosphorylated forms of lipid A in Gram-negative bacteria using a multivaried mass spectrometric approach
- PMID: 18753624
- PMCID: PMC2529124
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0800445105
Determination of pyrophosphorylated forms of lipid A in Gram-negative bacteria using a multivaried mass spectrometric approach
Abstract
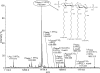
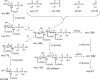
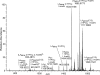
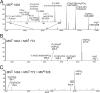
Lipid A isolated from several bacteria (Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella enterica, and various strains of Yersinia) showed abundant formation of pyrophosphate anions upon ion dissociation. Pyrophosphate [H(3)P(2)O(7)](-) and/or [HP(2)O(6)](-) anions were observed as dominant fragments from diphosphorylated lipid A anions regardless of the ionization mode (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization or electrospray ionization), excitation mode (collisional activation or infrared photoexcitation), or mass analyzer (time-of-flight/time-of-flight, tandem quadrupole, Fourier transform-ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry). Dissociations of anions from model lipid phosphate, pyrophosphate, and hexose diphosphates confirmed that pyrophosphate fragments were formed abundantly only in the presence of an intact pyrophosphate group in the analyte molecule and were not due to intramolecular rearrangement upon ionization, ion-molecule reactions, or rearrangement following activation. This indicated that pyrophosphate groups are present in diphosphorylated lipid A from a variety of Gram-negative bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Trent MS. Biosynthesis, transport, and modification of lipid A. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004;82:71–86. - PubMed
-
- Ernst RK, Guina T, Miller SI. How intracellular bacteria survive: Surface modifications that promote resistance to host innate immune responses. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl 2):S326–S330. - PubMed
-
- Guo L, et al. Lipid A acylation and bacterial resistance against vertebrate antimicrobial peptides. Cell. 1998;95:189–198. - PubMed
-
- Miller SI, Ernst RK, Bader MW. LPS, TLR4, and infectious disease diversity. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:36–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

