Structure-guided inhibitor design for human FAAH by interspecies active site conversion
- PMID: 18753625
- PMCID: PMC2529035
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806121105
Structure-guided inhibitor design for human FAAH by interspecies active site conversion
Abstract
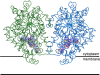
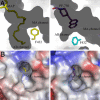
The integral membrane enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) hydrolyzes the endocannabinoid anandamide and related amidated signaling lipids. Genetic or pharmacological inactivation of FAAH produces analgesic, anxiolytic, and antiinflammatory phenotypes but not the undesirable side effects of direct cannabinoid receptor agonists, indicating that FAAH may be a promising therapeutic target. Structure-based inhibitor design has, however, been hampered by difficulties in expressing the human FAAH enzyme. Here, we address this problem by interconverting the active sites of rat and human FAAH using site-directed mutagenesis. The resulting humanized rat (h/r) FAAH protein exhibits the inhibitor sensitivity profiles of human FAAH but maintains the high-expression yield of the rat enzyme. We report a 2.75-A crystal structure of h/rFAAH complexed with an inhibitor, N-phenyl-4-(quinolin-3-ylmethyl)piperidine-1-carboxamide (PF-750), that shows strong preference for human FAAH. This structure offers compelling insights to explain the species selectivity of FAAH inhibitors, which should guide future drug design programs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
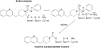
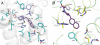
References
-
- Cravatt BF, et al. Molecular characterization of an enzyme that degrades neuromodulatory fatty-acid amides. Nature. 1996;384:83–87. - PubMed
-
- McKinney MK, Cravatt BF. Structure and function of fatty acid amide hydrolase. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:411–432. - PubMed
-
- Devane WA, et al. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science. 1992;258:1946–1949. - PubMed
-
- Lambert DM, Vandevoorde S, Jonsson KO, Fowler CJ. The palmitoylethanolamide family: A new class of antiinflammatory agents? Curr Med Chem. 2002;9:663–674. - PubMed
-
- Cravatt BF, et al. Chemical characterization of a family of brain lipids that induce sleep. Science. 1995;268:1506–1509. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

