Lack of evidence for activation of the hedgehog pathway in psoriasis
- PMID: 18754037
- PMCID: PMC2771222
- DOI: 10.1038/jid.2008.266
Lack of evidence for activation of the hedgehog pathway in psoriasis
Abstract
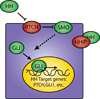
Recent reports have suggested that the hedgehog (Hh) pathway is activated in lesional psoriatic skin, and that treatment with the Hh pathway antagonist cyclopamine may lead to rapid resolution of the disease. To assess Hh pathway activity in psoriasis, we isolated RNA from lesional and uninvolved skin of 58 psoriatic patients, and from 63 normal control subjects, and subjected these samples to global gene expression profiling on Affymetrix HU133 Plus 2.0 gene arrays. We were especially interested in Hh target genes (PTCH1 and GLI1), whose expression is elevated in response to Hh signaling. The microarray data demonstrated downregulation of PTCH1 expression in uninvolved and lesional skin (1.1-fold and 2-fold, respectively; P<0.0001). Additionally GLI1 mRNA was downregulated in lesional skin (1.7 fold; P<0.05). No significant changes were observed between lesional and uninvolved skin for the Hh ligands or Smoothened. Quantitative PCR confirmed these findings. In situ hybridization for GLI1 and PTCH1 was positive in basal cell carcinoma tumor cells, but was negligible in uninvolved or lesional psoriatic skin. The absence of elevated Hh target gene expression in lesional psoriatic skin indicates that the Hh pathway is not activated in this disease, raising questions regarding the proposed use of Hh antagonists as antipsoriatic agents.
References
-
- Belloni E, Muenke M, Roessler E, Traverso G, Siegel-Bartelt J, Frumkin A, Mitchell HF, Donis-Keller H, Helms C, Hing AV, Heng HH, Koop B, Martindale D, Rommens JM, Tsui LC, Scherer SW. Identification of Sonic hedgehog as a candidate gene responsible for holoprosencephaly. Nat Genet. 1996;14:353–356. - PubMed
-
- Bowcock AM, Krueger JG. Getting under the skin: the immunogenetics of psoriasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:699–711. - PubMed
-
- Bowcock AM, Shannon W, Du F, Duncan J, Cao K, Aftergut K, Catier J, Fernandez-Vina MA, Menter A. Insights into psoriasis and other inflammatory diseases from large-scale gene expression studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:1793–1805. - PubMed
-
- Chan VS, Chau SY, Tian L, Chen Y, Kwong SK, Quackenbush J, Dallman M, Lamb J, Tam PK. Sonic hedgehog promotes CD4+ T lymphocyte proliferation and modulates the expression of a subset of CD28-targeted genes. Int Immunol. 2006;18:1627–1636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical