FERN - a Java framework for stochastic simulation and evaluation of reaction networks
- PMID: 18755046
- PMCID: PMC2553347
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-356
FERN - a Java framework for stochastic simulation and evaluation of reaction networks
Abstract
Background: Stochastic simulation can be used to illustrate the development of biological systems over time and the stochastic nature of these processes. Currently available programs for stochastic simulation, however, are limited in that they either a) do not provide the most efficient simulation algorithms and are difficult to extend, b) cannot be easily integrated into other applications or c) do not allow to monitor and intervene during the simulation process in an easy and intuitive way. Thus, in order to use stochastic simulation in innovative high-level modeling and analysis approaches more flexible tools are necessary.
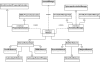
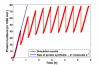
Results: In this article, we present FERN (Framework for Evaluation of Reaction Networks), a Java framework for the efficient simulation of chemical reaction networks. FERN is subdivided into three layers for network representation, simulation and visualization of the simulation results each of which can be easily extended. It provides efficient and accurate state-of-the-art stochastic simulation algorithms for well-mixed chemical systems and a powerful observer system, which makes it possible to track and control the simulation progress on every level. To illustrate how FERN can be easily integrated into other systems biology applications, plugins to Cytoscape and CellDesigner are included. These plugins make it possible to run simulations and to observe the simulation progress in a reaction network in real-time from within the Cytoscape or CellDesigner environment.
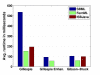
Conclusion: FERN addresses shortcomings of currently available stochastic simulation programs in several ways. First, it provides a broad range of efficient and accurate algorithms both for exact and approximate stochastic simulation and a simple interface for extending to new algorithms. FERN's implementations are considerably faster than the C implementations of gillespie2 or the Java implementations of ISBJava. Second, it can be used in a straightforward way both as a stand-alone program and within new systems biology applications. Finally, complex scenarios requiring intervention during the simulation progress can be modelled easily with FERN.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Stochastic P systems and the simulation of biochemical processes with dynamic compartments.Biosystems. 2008 Mar;91(3):458-72. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2006.12.009. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Biosystems. 2008. PMID: 17728055 Review.
-
MONALISA for stochastic simulations of Petri net models of biochemical systems.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Jul 10;16:215. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0596-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 26156221 Free PMC article.
-
Design and implementation of a tool for translating SBML into the biochemical stochastic pi-calculus.Bioinformatics. 2006 Dec 15;22(24):3075-81. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl516. Epub 2006 Oct 17. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17046974
-
Hybrid stochastic simplifications for multiscale gene networks.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 Sep 7;3:89. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-89. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19735554 Free PMC article.
-
Modelling metapopulations with stochastic membrane systems.Biosystems. 2008 Mar;91(3):499-514. doi: 10.1016/j.biosystems.2006.12.011. Epub 2007 Aug 11. Biosystems. 2008. PMID: 17904729 Review.
Cited by
-
The challenges of informatics in synthetic biology: from biomolecular networks to artificial organisms.Brief Bioinform. 2010 Jan;11(1):80-95. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbp054. Epub 2009 Nov 11. Brief Bioinform. 2010. PMID: 19906839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BioSANS: A software package for symbolic and numeric biological simulation.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 18;17(4):e0256409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256409. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35436294 Free PMC article.
-
Transfer functions for protein signal transduction: application to a model of striatal neural plasticity.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e55762. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0055762. Epub 2013 Feb 6. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23405211 Free PMC article.
-
Sequestration of CaMKII in dendritic spines in silico.J Comput Neurosci. 2011 Nov;31(3):581-94. doi: 10.1007/s10827-011-0323-2. Epub 2011 Apr 14. J Comput Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21491127
-
A travel guide to Cytoscape plugins.Nat Methods. 2012 Nov;9(11):1069-76. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2212. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Nat Methods. 2012. PMID: 23132118 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szallasi Z, Stelling J, Periwal V. System Modeling in Cellular Biology. MIT Press; 2006.
-
- Gillespie DT. A general method for numerically simulating the stochastic time evolution of coupled chemical reactions. Journal of Computational Physics. 1976;22:403–434. doi: 10.1016/0021-9991(76)90041-3. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

