Defects of prostate development and reproductive system in the estrogen receptor-alpha null male mice
- PMID: 18755802
- PMCID: PMC5398428
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2008-0044
Defects of prostate development and reproductive system in the estrogen receptor-alpha null male mice
Abstract
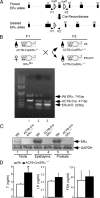
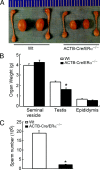
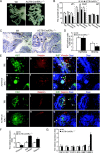
The estrogen receptor-alpha knockout (ERalphaKO, ERalpha-/-) mice were generated via the Cre-loxP system by mating floxed ERalpha mice with beta-actin (ACTB)-Cre mice. The impact of ERalpha gene deletion in the male reproductive system was investigated. The ACTB-Cre/ERalpha(-/-) male mice are infertile and have lost 90% of epididymal sperm when compared with wild-type mice. Serum testosterone levels in ACTB-Cre/ERalpha(-/-) male mice are 2-fold elevated. The ACTB-Cre/ERalpha(-/-) testes consist of atrophic and degenerating seminiferous tubules with less cellularity in the disorganized seminiferous epithelia. Furthermore, the ventral and dorsal-lateral prostates of ACTB-Cre/ERalpha(-/-) mice display reduced branching morphogenesis. Loss of ERalpha could also be responsible for the decreased fibroblast proliferation and changes in the stromal content. In addition, we found bone morphogenetic protein, a mesenchymal inhibitor of prostatic branching morphogenesis, is significantly up-regulated in the ACTB-Cre/ERalpha(-/-) prostates. Collectively, these results suggest that ERalpha is required for male fertility, acts through a paracrine mechanism to regulate prostatic branching morphogenesis, and is involved in the proliferation and differentiation of prostatic stromal compartment.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reduced prostate branching morphogenesis in stromal fibroblast, but not in epithelial, estrogen receptor α knockout mice.Asian J Androl. 2012 Jul;14(4):546-55. doi: 10.1038/aja.2011.181. Epub 2012 May 21. Asian J Androl. 2012. PMID: 22609821 Free PMC article.
-
Generation and characterization of a complete null estrogen receptor alpha mouse using Cre/LoxP technology.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Jan;321(1-2):145-53. doi: 10.1007/s11010-008-9928-9. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 18953638 Free PMC article.
-
Ex3αERKO male infertility phenotype recapitulates the αERKO male phenotype.J Endocrinol. 2010 Dec;207(3):281-8. doi: 10.1677/JOE-10-0290. Epub 2010 Sep 10. J Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 20833731 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Eralpha and ERbeta in the prostate: insights from genetic models and isoform-selective ligands.Ernst Schering Found Symp Proc. 2006;(1):131-47. doi: 10.1007/2789_2006_020. Ernst Schering Found Symp Proc. 2006. PMID: 17824175 Review.
-
Estrogenic effects on prostatic differentiation and carcinogenesis.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2001;13(4):285-96. doi: 10.1071/rd01010. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2001. PMID: 11800167 Review.
Cited by
-
TEX11 modulates germ cell proliferation by competing with estrogen receptor β for the binding to HPIP.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Apr;26(4):630-42. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1263. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22383461 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of androgen receptor binding and transcriptomic analysis in mesenchymal subsets during prostate development.Dis Model Mech. 2019 Jul 25;12(7):dmm039297. doi: 10.1242/dmm.039297. Dis Model Mech. 2019. PMID: 31350272 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor α in cancer-associated fibroblasts suppresses prostate cancer invasion via modulation of thrombospondin 2 and matrix metalloproteinase 3.Carcinogenesis. 2014 Jun;35(6):1301-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt488. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Carcinogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24374826 Free PMC article.
-
Expression pattern of estrogen receptors α and β and G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 in the human testis.Histochem Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;142(4):421-32. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1216-z. Epub 2014 Apr 2. Histochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24692005
-
Ontogeny of estrogen receptors in human male and female fetal reproductive tracts.Differentiation. 2021 Mar-Apr;118:107-131. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2020.10.001. Epub 2020 Oct 17. Differentiation. 2021. PMID: 33176961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Couse JF, Korach KS 1999. Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr Rev 20:358–417 - PubMed
-
- Liu MM, Albanese C, Anderson CM, Hilty K, Webb P, Uht RM, Price Jr RH, Pestell RG, Kushner PJ 2002. Opposing action of estrogen receptors α and β on cyclin D1 gene expression. J Biol Chem 277:24353–24360 - PubMed
-
- Paech K, Webb P, Kuiper GG, Nilsson S, Gustafsson J, Kushner PJ, Scanlan TS 1997. Differential ligand activation of estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ at AP1 sites. Science 277:1508–1510 - PubMed
-
- Kuiper GG, Carlsson B, Grandien K, Enmark E, Haggblad J, Nilsson S, Gustafsson JA 1997. Comparison of the ligand binding specificity and transcript tissue distribution of estrogen receptors α and β. Endocrinology 138:863–870 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

