Chromatin-bound mitogen-activated protein kinases transmit dynamic signals in transcription complexes in beta-cells
- PMID: 18755896
- PMCID: PMC2533187
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0806465105
Chromatin-bound mitogen-activated protein kinases transmit dynamic signals in transcription complexes in beta-cells
Abstract
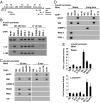
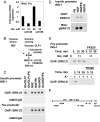
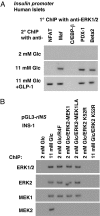
MAPK pathways regulate transcription through phosphorylation of transcription factors and other DNA-binding proteins. In pancreatic beta-cells, ERK1/2 are required for transcription of the insulin gene and several other genes in response to glucose. We show that binding of glucose-sensitive transcription activators and repressors to the insulin gene promoter depends on ERK1/2 activity. We also find that glucose and NGF stimulate the binding of ERK1/2 to the insulin gene and other promoters. An ERK1/2 cascade module, including MEK1/2 and Rsk, are found in complexes bound to these promoters. These findings imply that MAPK-containing signaling complexes are positioned on sensitive promoters with their protein substrates to modulate transcription in situ in response to incoming signals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Khoo S, et al. Regulation of insulin gene transcription by extracellular-signal regulated protein kinases (ERK) 1 and 2 in pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:32969–32977. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence MC, McGlynn K, Park BH, Cobb MH. ERK1/2- dependent activation of transcription factors required for acute and chronic effects of glucose on the insulin gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:26751–26759. - PubMed
-
- Ohneda K, Ee H, German M. Regulation of insulin gene transcription. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2000;11:227–233. - PubMed
-
- Arnette D, et al. Regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 by glucose and peptide hormones in pancreatic beta cells. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:32517–32525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

