miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis
- PMID: 18755897
- PMCID: PMC2533205
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0801613105
miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis
Abstract
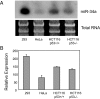
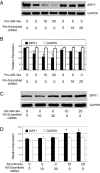
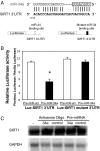
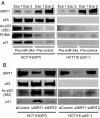
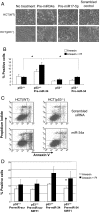
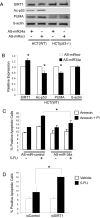
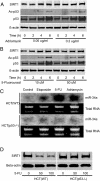
MicroRNA 34a (miR-34a) is a tumor suppressor gene, but how it regulates cell proliferation is not completely understood. We now show that the microRNA miR-34a regulates silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) expression. MiR-34a inhibits SIRT1 expression through a miR-34a-binding site within the 3' UTR of SIRT1. MiR-34 inhibition of SIRT1 leads to an increase in acetylated p53 and expression of p21 and PUMA, transcriptional targets of p53 that regulate the cell cycle and apoptosis, respectively. Furthermore, miR-34 suppression of SIRT1 ultimately leads to apoptosis in WT human colon cancer cells but not in human colon cancer cells lacking p53. Finally, miR-34a itself is a transcriptional target of p53, suggesting a positive feedback loop between p53 and miR-34a. Thus, miR-34a functions as a tumor suppressor, in part, through a SIRT1-p53 pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rigaud G, et al. Allelotype of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2000;88:772–777. - PubMed
-
- Bello MJ, et al. Allelic status of chromosome 1 in neoplasms of the nervous system. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1995;83:160–164. - PubMed
-
- Moley JF, et al. Consistent association of 1p loss of heterozygosity with pheochromocytomas from patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 syndromes. Cancer Res. 1992;52:770–774. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

