The prognostic significance of multiple station N2 in patients with surgically resected stage IIIA N2 non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 18756045
- PMCID: PMC2526397
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.604
The prognostic significance of multiple station N2 in patients with surgically resected stage IIIA N2 non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
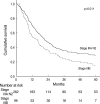
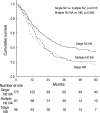
Mediastinal (N2) lymph node involvement is heterogeneous with huge variation in the extent and grouped together under stage IIIA. However, they showed a different survival even in the same stage. We tried to determine the prognostic implication of the multiple station N2 lymph node metastasis in stage IIIA N2 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The survival of stage IIIA N2 was analyzed according to the number of N2 station and their survival was compared with that of stage IIIB. In stage IIIA N2 NSCLC, multivariate analysis indicated that multiple station N2 was one of the independent prognostic factors for poor survival. The 5-yr survival of multiple station N2 IIIA (20.4%) was lower than that of single station N2 IIIA (33.8%) significantly (p=0.016). but when it was compared with that of stage IIIB (15.5%), there was no difference. Therefore, we suggest that multiple station N2 should be considered similar to stage IIIB disease with regard to predicting survival and accordingly should receive a new position in the TNM staging system.
Figures
References
-
- Naruke T, Tsuchiya R, Kondo H, Asamura H. Prognosis and survival after resection for bronchogenic carcinoma based on the 1997 TNM-staging classification: the Japanese experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;71:1759–1764. - PubMed
-
- Keller SM, Adak S, Wagner H, Johnson DH. Mediastinal lymph node dissection improves survival in patients with stage II and IIIA non-small cell lung cancer. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000;70:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Grunenwald D, Le Chevalier T. Re: Stage IIIA category of non-small cell lung cancer: a new proposal. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997;89:88–89. - PubMed
-
- Pearson FG, Delarue NC, Ilves R, Todd TR, Cooper JD. Significance of positive superior mediastinal nodes identified at mediastinoscopy in patients with resectable cancer of the lung. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1982;83:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Andre F, Grunenwald D, Pignon JP, Dujon A, Pujol JL, Brichon PY, Brouchet L, Quoix E, Westeel V, Le Chevalier T. Survival of patients with resected N2 non-small-cell lung cancer: evidence for a subclassification and implications. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:2981–2989. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical