Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 controls growth and cell cycle progression in human uterine leiomyoma
- PMID: 18756055
- PMCID: PMC2526409
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.667
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 controls growth and cell cycle progression in human uterine leiomyoma
Abstract
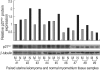
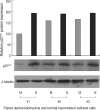
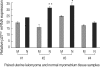
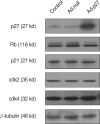
The molecular mechanism of the cell-cycle machinery in uterine leiomyoma has not yet been fully elucidated. Among the various types of cell-cycle regulators, p27(Kip1) (p27) is considered to be a potent tumor suppressor. To provide further molecular basis for understanding the progression of uterine leiomyoma, our objective was to evaluate the expression level of p27 in normal myometrium and uterine leiomyoma tissue and its effect on cytogenic growth. Western blot analysis, real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and immunohistochemical staining revealed that p27 protein and messenger RNA were down-regulated in uterine leiomyoma tissue and cultured cells compared to normal myometrium. Full-length human p27 cDNA was transferred using a replication-deficient recombinant adenoviral vector (Ad.p27) into uterine leiomyoma cells and evaluated the effect on cell proliferation. Transfection of Ad.p27 into uterine leiomyoma cells resulted in the induction of apoptosis, reduction in viability and proliferation of uterine leiomyoma cells. Our results suggest a new paradigm that down-regulated p27 protein expression is the possible underlying mechanism for the growth of uterine leiomyoma and over-expression of p27 induces cell death. This study provides better understanding of the control exerted by p27 in regulating growth and disease progression of uterine leiomyoma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antitumor effects of flavopiridol on human uterine leiomyoma in vitro and in a xenograft model.Reprod Sci. 2014 Sep;21(9):1153-60. doi: 10.1177/1933719114525266. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Reprod Sci. 2014. PMID: 24572052 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-150-5p May Contribute to Pathogenesis of Human Leiomyoma via Regulation of the Akt/p27Kip1 Pathway In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 31;20(11):2684. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112684. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31159158 Free PMC article.
-
An essential role of p27 downregulation in fenvalerate-induced cell growth in human uterine leiomyoma and smooth muscle cells.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Oct 15;303(8):E1025-35. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00107.2012. Epub 2012 Jul 31. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22850687 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of cyclin g1 expression in human uterine leiomyoma cells induces apoptosis.Reprod Sci. 2008 Apr;15(4):400-10. doi: 10.1177/1933719107314063. Reprod Sci. 2008. PMID: 18497347
-
Heparin inhibits proliferation of myometrial and leiomyomal smooth muscle cells through the induction of alpha-smooth muscle actin, calponin h1 and p27.Mol Hum Reprod. 1999 Feb;5(2):139-45. doi: 10.1093/molehr/5.2.139. Mol Hum Reprod. 1999. PMID: 10065869
Cited by
-
Antitumor effects of flavopiridol on human uterine leiomyoma in vitro and in a xenograft model.Reprod Sci. 2014 Sep;21(9):1153-60. doi: 10.1177/1933719114525266. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Reprod Sci. 2014. PMID: 24572052 Free PMC article.
-
Ulipristal acetate induces cell cycle delay and remodeling of extracellular matrix.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Oct;42(4):1857-1864. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3779. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30015921 Free PMC article.
-
An endocrine-disrupting chemical, fenvalerate, induces cell cycle progression and collagen type I expression in human uterine leiomyoma and myometrial cells.Toxicol Lett. 2010 Jul 15;196(3):133-41. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.03.004. Epub 2010 Mar 15. Toxicol Lett. 2010. PMID: 20230880 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-150-5p May Contribute to Pathogenesis of Human Leiomyoma via Regulation of the Akt/p27Kip1 Pathway In Vitro.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 31;20(11):2684. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112684. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31159158 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence-Based Management of Uterine Fibroids With Botanical Drugs-A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 22;13:878407. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.878407. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35800452 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Buttram VC, Reiter RC. Uterine leiomyomata: etiology, symptomatology, and management. Fertil Steril. 1981;36:433–445. - PubMed
-
- Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes Dev. 1999;13:1501–1512. - PubMed
-
- Tchernev G, Orfanos CE. Downregulation of cell cycle modulators p21, p27, p53, Rb and proapoptotic Bcl-2-related proteins Bax and Bak in cutaneous melanoma is associated with worse patient prognosis: preliminary findings. J Cutan Pathol. 2007;34:247–256. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda Y, Ichida T. p16 and p27 are functionally correlated during the progress of hepatocarcinogenesis. Med Mol Morphol. 2006;39:169–175. - PubMed
-
- Shariat SF, Ashfaq R, Sagalowsky AI, Lotan Y. Predictive value of cell cycle biomarkers in nonmuscle invasive bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol. 2007;177:481–487. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

