The interaction of gabapentin and N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine R-(-)isomer (R-PIA) on mechanical allodynia in rats with a spinal nerve ligation
- PMID: 18756057
- PMCID: PMC2526387
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2008.23.4.678
The interaction of gabapentin and N6-(2-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine R-(-)isomer (R-PIA) on mechanical allodynia in rats with a spinal nerve ligation
Abstract
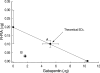
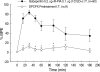
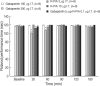
We examined the antiallodynic interaction between gabapentin and adenosine A1 receptor agonist, N(6)-(2-phenylisopropyl)-adenosine R-(-)isomer (R-PIA), in a rat model of nerve ligation injury. Rats were prepared with ligation of left L5-6 spinal nerves and intrathecal catheter implantation for drug administration. Mechanical allodynia was measured by applying von Frey filaments. Gabapentin and R-PIA were administered to obtain the dose-response curve and the 50% effective dose (ED(50)). Fractions of ED(50)s were administered concurrently to establish the ED(50) of the drug combination. The drug interaction between gabapentin and R-PIA was analyzed using the isobolographic method. Adenosine A1 receptor antagonist was administered intrathecally to examine the reversal of the antiallodynic effect. Locomotor function changes were evaluated by rotarod testing. Intrathecal gabapentin and R-PIA and their combination produced a dose-dependent antagonism against mechanical allodynia without severe side effects. Intrathecal gabapentin synergistically enhanced the antiallodynic effect of R-PIA when coadministered. There were no significant changes in rotarod performance time, except gabapentin 300 microg. In the combination group, the maximal antiallodynic effect was reversed by A1 adenosine receptor antagonist. These results suggest that activation of adenosine A1 receptors at the spinal level is required for the synergistic interaction on the mechanical allodynia.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antiallodynic and anti-inflammatory effects of intrathecal R-PIA in a rat model of vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2020 Oct;73(5):434-444. doi: 10.4097/kja.19481. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32046474 Free PMC article.
-
Morphine can enhance the antiallodynic effect of intrathecal R-PIA in rats with nerve ligation injury.Anesth Analg. 2005 Feb;100(2):461-468. doi: 10.1213/01.ANE.0000143561.68417.70. Anesth Analg. 2005. PMID: 15673876
-
Intrathecal gabapentin and clonidine synergistically inhibit allodynia in spinal nerve-ligated rats.Life Sci. 2010 Oct 23;87(17-18):565-71. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2010.09.017. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20875433
-
Synergistic effect between intrathecal non-NMDA antagonist and gabapentin on allodynia induced by spinal nerve ligation in rats.Anesthesiology. 2000 Feb;92(2):500-6. doi: 10.1097/00000542-200002000-00033. Anesthesiology. 2000. PMID: 10691238
-
Pharmacology of the spinal adenosine receptor which mediates the antiallodynic action of intrathecal adenosine agonists.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996 Jun;277(3):1642-8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1996. PMID: 8667233
Cited by
-
Intrathecal gabapentin increases interleukin-10 expression and inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine in a rat model of neuropathic pain.J Korean Med Sci. 2013 Feb;28(2):308-14. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.2.308. Epub 2013 Jan 29. J Korean Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 23399960 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential of Gabapentin with a Focus on Topical Formulations to Treat Ocular Surface Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 11;17(5):623. doi: 10.3390/ph17050623. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiallodynic and anti-inflammatory effects of intrathecal R-PIA in a rat model of vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2020 Oct;73(5):434-444. doi: 10.4097/kja.19481. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32046474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kim SH, Chung JM. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain. 1992;50:355–363. - PubMed
-
- Kim KJ, Yoon YW, Chung JM. Comparison of three rodent neuropathic pain models. Exp Brain Res. 1997;113:200–206. - PubMed
-
- Ralevic V, Burnstock G. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev. 1998;50:413–492. - PubMed
-
- Sawynok J. Adenosine receptor activation and nociception. Eur J Pharmacol. 1998;347:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Sawynok J. Purines in pain management. Curr Opin CPNS Invest Drugs. 1999;1:27–38.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

