Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy: which way to go?
- PMID: 18756599
- PMCID: PMC2739944
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.4909
Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy: which way to go?
Abstract
Aim: To compare the outcome of laparoscopic versus open appendectomy.
Methods: Prospectively collected data from 293 consecutive patients with acute appendicitis were studied. These comprised of 165 patients who underwent conventional appendectomy and 128 patients treated laparoscopically. The two groups were compared with respect to operative time, length of hospital stay, postoperative pain, complication rate and cost.
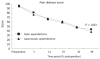
Results: There were no statistical differences regarding patient characteristics between the two groups. Conversion to laparotomy was necessary in 2 patients (1.5%). Laparoscopic appendectomy was associated with a shorter hospital stay (2.2 d vs 3.1 d, P = 0.04), and lower incidence of wound infection (5.3% vs 12.8%, P = 0.03). However, in patients with complicated disease, intra-abdominal abscess formation was more common after laparoscopic appendectomy (5.3% vs 2.1%, P = 0.002). The operative time and analgesia requirements were similar in the two groups. The cost of treatment was higher by 370 EUR in the laparoscopic group.
Conclusion: Laparoscopic appendectomy is as safe and efficient as open appendectomy, provided surgical experience and equipment are available.
Figures
References
-
- Semm K. Endoscopic appendectomy. Endoscopy. 1983;15:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Kurtz RJ, Heimann TM. Comparison of open and laparoscopic treatment of acute appendicitis. Am J Surg. 2001;182:211–214. - PubMed
-
- Wullstein C, Barkhausen S, Gross E. Results of laparoscopic vs. conventional appendectomy in complicated appendicitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001;44:1700–1705. - PubMed
-
- Fogli L, Brulatti M, Boschi S, Di Domenico M, Papa V, Patrizi P, Capizzi FD. Laparoscopic appendectomy for acute and recurrent appendicitis: retrospective analysis of a single-group 5-year experience. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2002;12:107–110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical