Detection and localization of single LysM-peptidoglycan interactions
- PMID: 18757536
- PMCID: PMC2580685
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00519-08
Detection and localization of single LysM-peptidoglycan interactions
Abstract
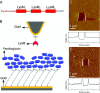
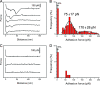
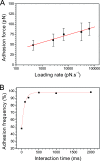
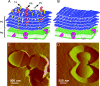
The lysin motif (LysM) is a ubiquitous protein module that binds peptidoglycan and structurally related molecules. Here, we used single-molecule force spectroscopy (SMFS) to measure and localize individual LysM-peptidoglycan interactions on both model and cellular surfaces. LysM modules of the major autolysin AcmA of Lactococcus lactis were bound to gold-coated atomic force microscopy tips, while peptidoglycan was covalently attached onto model supports. Multiple force curves recorded between the LysM tips and peptidoglycan surfaces yielded a bimodal distribution of binding forces, presumably reflecting the occurrence of one and two LysM-peptidoglycan interactions, respectively. The specificity of the measured interaction was confirmed by performing blocking experiments with free peptidoglycan. Next, the LysM tips were used to map single LysM interactions on the surfaces of L. lactis cells. Strikingly, native cells showed very poor binding, suggesting that peptidoglycan was hindered by other cell wall constituents. Consistent with this notion, treatment of the cells with trichloroacetic acid, which removes peptidoglycan-associated polymers, resulted in substantial and homogeneous binding of the LysM tip. These results provide novel insight into the binding forces of bacterial LysMs and show that SMFS is a promising tool for studying the heterologous display of proteins or peptides on bacterial surfaces.
Figures
Similar articles
-
AcmD, a homolog of the major autolysin AcmA of Lactococcus lactis, binds to the cell wall and contributes to cell separation and autolysis.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 8;8(8):e72167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0072167. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23951292 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of the binding activity of Lactococcus lactis peptidoglycan protein anchor with different number of motifs].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015 Feb 4;55(2):193-7. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 25958699 Chinese.
-
Determinants of murein hydrolase targeting to cross-wall of Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):10460-10471. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.336404. Epub 2012 Feb 2. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22303016 Free PMC article.
-
LysM, a widely distributed protein motif for binding to (peptido)glycans.Mol Microbiol. 2008 May;68(4):838-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06211.x. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18430080 Review.
-
Murein and pseudomurein cell wall binding domains of bacteria and archaea--a comparative view.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011 Dec;92(5):921-8. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3637-0. Epub 2011 Oct 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 22012341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel bacterium-like particles platform displaying antigens by new anchoring proteins induces efficacious immune responses.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 22;15:1395837. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1395837. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38841059 Free PMC article.
-
Critical cell wall hole size for lysis in Gram-positive bacteria.J R Soc Interface. 2013 Jan 9;10(80):20120892. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0892. Print 2013 Mar 6. J R Soc Interface. 2013. PMID: 23303219 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring kinetic dissociation/association constants between Lactococcus lactis bacteria and mucins using living cell probes.Biophys J. 2011 Dec 7;101(11):2843-53. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.10.034. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 22261074 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting the peptidoglycan-binding motif, LysM, for medical and industrial applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014 May;98(10):4331-45. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5633-7. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24652063 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging the nanoscale organization of peptidoglycan in living Lactococcus lactis cells.Nat Commun. 2010 Jun 15;1(3):27. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1027. Nat Commun. 2010. PMID: 20975688 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bateman, A., and M. Bycroft. 2000. The structure of a LysM domain from E. coli membrane-bound lytic murein transglycosylase D (MltD). J. Mol. Biol. 2991113-1119. - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner, W., H. Gruber, P. Hinterdorfer, and D. Drenckhahn. 2000. Affinity of trans-interacting VE-cadherin determined by atomic force microscopy. Single Mol. 1119-122.
-
- Bell, G. I. 1978. Models for the specific adhesion of cells to cells. Science 200618-627. - PubMed
-
- Birkeland, N. K. 1994. Cloning, molecular characterization, and expression of the genes encoding the lytic functions of lactococcal bacteriophage-Phi-Lc3—a dual lysis system of modular design. Can. J. Microbiol. 40658-665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

