Specific DNA binding of a potential transcriptional regulator, inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase-related protein VII, to the promoter region of a methyl coenzyme m reductase I-encoding operon retrieved from Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus strain DeltaH
- PMID: 18757575
- PMCID: PMC2570296
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02155-07
Specific DNA binding of a potential transcriptional regulator, inosine 5'-monophosphate dehydrogenase-related protein VII, to the promoter region of a methyl coenzyme m reductase I-encoding operon retrieved from Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus strain DeltaH
Abstract
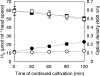
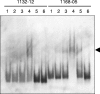
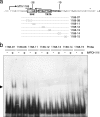
Two methyl coenzyme M reductases (MCRs) encoded by the mcr and mrt operons of the hydrogenotrophic methanogen Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus DeltaH are expressed in response to H(2) availability. In the present study, cis elements and trans-acting factors responsible for the gene expression of MCRs were investigated by using electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) and affinity particle purification. A survey of their operator regions by EMSA with protein extracts from mrt-expressing cultures restricted them to 46- and 41-bp-long mcr and mrt upstream regions, respectively. Affinity particle purification of DNA-binding proteins conjugated with putative operator regions resulted in the retrieval of a protein attributed to IMP dehydrogenase-related protein VII (IMPDH VII). IMPDH VII is predicted to have a winged helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif and two cystathionine beta-synthase domains, and it has been suspected to be an energy-sensing module. EMSA with oligonucleotide probes with unusual sequences showed that the binding site of IMPDH VII mostly overlaps the factor B-responsible element-TATA box of the mcr operon. The results presented here suggest that IMPDH VII encoded by MTH126 is a plausible candidate for the transcriptional regulator of the mcr operon in this methanogen.
Figures
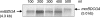


References
-
- Alex, L. A., J. N. Reeve, W. H. Orme-Johnson, and C. T. Walsh. 1990. Cloning, sequence determination, and expression of the genes encoding the subunits of the nickel-containing 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin reducing hydrogenase from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum ΔH. Biochemistry 29:7237-7244. - PubMed
-
- Bernhard, M., T. Buhrke, B. Bleijlevens, A. L. De Lacey, V. M. Fernandez, S. P. Albracht, and B. Friedrich. 2001. The H2 sensor of Ralstonia eutropha. Biochemical characteristics, spectroscopic properties, and its interaction with a histidine protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 276:15592-15597. - PubMed
-
- Blair, E., C. Redwood, H. Ashrafian, M. Oliveira, J. Broxholme, B. Kerr, A. Salmon, I. Östman-Smith, and H. Watkins. 2001. Mutations in the γ2 subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: evidence for the central role of energy compromise in disease pathogenesis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10:1215-1220. - PubMed
-
- Bonacker, L. G., S. Baudner, E. Morschel, R. Bocher, and R. K. Thauer. 1993. Properties of the two isoenzymes of methyl-coenzyme M reductase in Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Eur. J. Biochem. 217:587-595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

