Clozapine and sulpiride but not haloperidol or olanzapine activate brain DNA demethylation
- PMID: 18757738
- PMCID: PMC2533238
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0805493105
Clozapine and sulpiride but not haloperidol or olanzapine activate brain DNA demethylation
Abstract
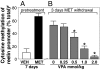
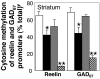
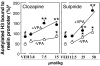
Cortical GABAergic dysfunction, a hallmark of both schizophrenia (SZ) and bipolar (BP) disorder pathophysiologies may relate to the hypermethylation of GABAergic gene promoters (i.e., reelin and GAD67). Benefits elicited by a combination of atypical antipsychotics with valproate (VPA) (a histone deacetylase inhibitor that may also activate brain DNA demethylation) in SZ or BP disorder treatment prompted us to investigate whether the beneficial action of this association depends on induction of a putative DNA demethylase activity. To monitor this activity, we measured the ratio of 5-methyl cytosine to unmethylated cytosine in reelin and GAD67 promoters in the mouse frontal cortex and striatum. We compared normal mice with mice pretreated with l-methionine (5.2 mmol/kg s.c. twice a day for 7 days) to hypermethylate promoters, including reelin and GAD67. Clinically relevant doses of clozapine (CLZ) (3.8 to 15 micromol/kg twice a day s.c. for 3 days) and sulpiride (SULP) (12.5 to 50 micromol/kg twice a day for 3 days) but not clinically relevant doses of haloperidol (HAL) (1.3 to 4 micromol/kg twice a day s.c. for 3 days) or olanzapine (OLZ) (4 to 15 micromol/kg twice a day for 3 days) exhibited dose-related increases in the cortical and striatal demethylation of hypermethylated reelin and GAD67 promoters. These effects of CLZ and SULP were dramatically potentiated by a clinically relevant VPA dose (0.5 mmol/kg twice a day for 3 days). By activating a DNA demethylase, the association of CLZ or SULP with VPA may facilitate a chromatin remodeling that normalizes the GABAergic gene expression down-regulation detected in the telencephalic regions of SZ and BP patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Akbarian S, et al. Gene expression for glutamic acid decarboxylase is reduced without loss of neurons in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1995;562:258–266. - PubMed
-
- Lewis DA, Hashimoto T, Volk DW. Cortical inhibitory neurons and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:312–324. - PubMed
-
- Guidotti A, et al. Decreased reelin and glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) expression in schizophrenia and bipolar disorders: A postmortem brain study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2000;57:1061–1069. - PubMed
-
- Woo T-U W, Walsh JP, Benes FM. Density of glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 messenger RNA-containing neurons that express the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit NR2A in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004;61:649–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

