Transmission dynamics of heritable silencing induced by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 18757930
- PMCID: PMC2581934
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.108.089433
Transmission dynamics of heritable silencing induced by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
Heritable silencing effects are gene suppression phenomena that can persist for generations after induction. In the majority of RNAi experiments conducted in Caenorhabditis elegans, the silencing response results in a hypomorphic phenotype where the effects recede after the F1 generation. F2 and subsequent generations revert to the original phenotype. Specific examples of transgenerational RNAi in which effects persist to the F2 generation and beyond have been described. In this study, we describe a systematic pedigree-based analysis of heritable silencing processes resulting from initiation of interference targeted at the C. elegans oocyte maturation factor oma-1. Heritable silencing of oma-1 is a dose-dependent process where the inheritance of the silencing factor is unequally distributed among the population. Heritability is not constant over generational time, with silenced populations appearing to undergo a bottleneck three to four generations following microinjection of RNA. Transmission of silencing through these generations can be through either maternal or paternal gamete lines and is surprisingly more effective through the male gametic line. Genetic linkage tests reveal that silencing in the early generations is transmitted independently of the original targeted locus, in a manner indicative of a diffusible epigenetic element.
Figures

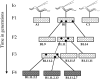
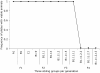

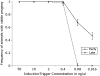
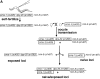





References
-
- Alleman, M., L. Sidorenko, K. McGinnis, V. Seshadri, J. E. Dorweiler et al., 2006. An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is required for paramutation in maize. Nature 442 295–298. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, E., A. A. Caudy, S. M. Hammond and G. J. Hannon, 2001. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature 409 363–366. - PubMed
-
- Chandler, V. L., 2007. Paramutation: from maize to mice. Cell 128 641–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

