A novel chimeric low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit gene from the wild relatives of wheat Aegilops kotschyi and Ae. juvenalis: evolution at the Glu-3 loci
- PMID: 18757939
- PMCID: PMC2535725
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.108.092403
A novel chimeric low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit gene from the wild relatives of wheat Aegilops kotschyi and Ae. juvenalis: evolution at the Glu-3 loci
Abstract
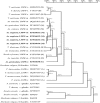
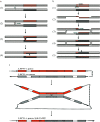
Four LMW-m and one novel chimeric (between LMW-i and LMW-m types) low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit (LMW-GS) genes from Aegilops neglecta (UUMM), Ae. kotschyi (UUSS), and Ae. juvenalis (DDMMUU) were isolated and characterized. Sequence structures showed that the 4 LMW-m-type genes, assigned to the M genome of Ae. neglecta, displayed a high homology with those from hexaploid common wheat. The novel chimeric gene, designed as AjkLMW-i, was isolated from both Ae. kotschyi and Ae. juvenalis and shown to be located on the U genome. Phylogentic analysis demonstrated that it had higher identity to the LMW-m-type than the LMW-i-type genes. A total of 20 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were detected among the 4 LMW-m genes, with 13 of these being nonsynonymous SNPs that resulted in amino acid substitutions in the deduced mature proteins. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that it had higher identity to the LMW-m-type than the LMW-i-type genes. The divergence time estimation showed that the M and D genomes were closely related and diverged at 5.42 million years ago (MYA) while the differentiation between the U and A genomes was 6.82 MYA. We propose that, in addition to homologous recombination, an illegitimate recombination event on the U genome may have occurred 6.38 MYA and resulted in the generation of the chimeric gene AjkLMW-i, which may be an important genetic mechanism for the origin and evolution of LMW-GS Glu-3 alleles as well as other prolamin genes.
Figures


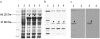
Similar articles
-
Phylogenetic relationship of a new class of LMW-GS genes in the M genome of Aegilops comosa.Theor Appl Genet. 2011 May;122(7):1411-25. doi: 10.1007/s00122-011-1541-8. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Theor Appl Genet. 2011. PMID: 21301802
-
Phylogenetic analysis of C, M, N, and U genomes and their relationships with Triticum and other related genomes as revealed by LMW-GS genes at Glu-3 loci.Genome. 2011 Apr;54(4):273-84. doi: 10.1139/g10-119. Genome. 2011. PMID: 21491971
-
Cloning and molecular characterization of three novel LMW-i glutenin subunit genes from cultivated einkorn (Triticum monococcum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2006 Aug;113(3):383-95. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0299-x. Epub 2006 Jun 15. Theor Appl Genet. 2006. PMID: 16775696
-
Molecular characterization and genomic organization of low molecular weight glutenin subunit genes at the Glu-3 loci in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Theor Appl Genet. 2008 May;116(7):953-66. doi: 10.1007/s00122-008-0727-1. Epub 2008 Feb 28. Theor Appl Genet. 2008. PMID: 18305921
-
Low molecular weight glutenin subunit gene composition at Glu-D3 loci of Aegilops tauschii and common wheat and a further view of wheat evolution.Theor Appl Genet. 2018 Dec;131(12):2745-2763. doi: 10.1007/s00122-018-3188-1. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Theor Appl Genet. 2018. PMID: 30225644
Cited by
-
Recruitment of closely linked genes for divergent functions: the seed storage protein (Glu-3) and powdery mildew (Pm3) genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Funct Integr Genomics. 2010 May;10(2):241-51. doi: 10.1007/s10142-009-0150-y. Epub 2009 Dec 12. Funct Integr Genomics. 2010. PMID: 20012664
-
Phylogenetic relationship of a new class of LMW-GS genes in the M genome of Aegilops comosa.Theor Appl Genet. 2011 May;122(7):1411-25. doi: 10.1007/s00122-011-1541-8. Epub 2011 Feb 8. Theor Appl Genet. 2011. PMID: 21301802
-
Molecular characterization and expression of α-gliadin genes from wheat cultivar Dacke in Bg 250 rice variety.GM Crops Food. 2019;10(2):102-114. doi: 10.1080/21645698.2019.1622990. Epub 2019 May 29. GM Crops Food. 2019. PMID: 31142188 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of low molecular weight glutenin subunit genes from Pseudoroegneria spicata and Pd. strigosa.J Appl Genet. 2015 Feb;56(1):27-35. doi: 10.1007/s13353-014-0229-6. Epub 2014 Aug 7. J Appl Genet. 2015. PMID: 25099921
-
The α-gliadin genes from Brachypodium distachyon L. provide evidence for a significant gap in the current genome assembly.Funct Integr Genomics. 2014 Mar;14(1):149-60. doi: 10.1007/s10142-013-0353-0. Epub 2013 Dec 7. Funct Integr Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24318766
References
-
- Allaby, R. G., M. Banerjee and T. A. Brown, 1999. Evolution of the high molecular weight glutenin loci of the A, B, D, and R genomes of wheat. Genome 42 296–307. - PubMed
-
- Allgood, N. D., and T. J. Silhavy, 1988. Illegitimate recombination in bacteria, pp. 309–330 in Genetic Recombination, edited by R. Kucherlapati and G. R. Simth. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
-
- An, X., Y. Yan, Y. Xiao, Q. Li, S. L.K. Hsam et al., 2005. Genetic diversity of European spelt wheat (Triticum spelta L.) revealed by glutenin subunit variations at Glu-1 and Glu-3 loci. Euphytica 146 193–201.
-
- An, X., Q. Zhang, Y. Yan, Q. Li, Y. Zhang et al., 2006. Cloning and molecular characterization of three novel LMW-i glutenin subunit genes from cultivatied einkorn (Triticum monococcum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 113 383–395. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, O. D., and F. C. Greene, 1989. The characterization and comparative analysis of high-molecular-weight glutenin genes from genomes A and B of a hexaploid bread wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 77 689–700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

