Southwest Oncology Group phase II trial (S0341) of erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and a performance status of 2
- PMID: 18758306
- PMCID: PMC3523698
- DOI: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318183aa1f
Southwest Oncology Group phase II trial (S0341) of erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer and a performance status of 2
Abstract
Purpose: This phase II study (S0341) evaluated the efficacy and tolerability of single-agent erlotinib in unselected chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and a performance status (PS) of 2. Exploratory analyses of a number of biomarkers relating to epidermal growth factor receptor pathway activation were also performed.
Patients and methods: Patients with stage IIIB (pleural effusion) or stage IV NSCLC with a PS of 2 and no prior chemotherapy or biologic treatment for NSCLC received erlotinib 150 mg daily.
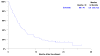
Results: A total of 81 patients entered the study; 76 were assessable. One complete and 5 partial responses were noted for an overall response rate of 8% (95% CI 3%-16%). Stable disease (SD) was seen in 26 patients (34%) resulting in a disease control rate (DCR = CR/PR/SD) of 42%. Progression free and median survival were 2.1 months (95% CI 1.5-3.1) and 5 months (95% CI 3.6-7.2), respectively. One-year survival was 24% (95% CI 15%-34%). Although treatment was generally well tolerated, grade 3 to 4 toxicity was reported in 30 patients (40%), including fatigue (16%), rash (9%), diarrhea (7%), and anorexia (7%). There was one possible treatment related death (pneumonitis).
Conclusions: In chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced NSCLC and a PS of 2, single agent erlotinib resulted in an acceptable but significant level of treatment-related side effects. With an overall DCR of 42% and median survival of 5 months, results are comparable to those achieved with chemotherapy in this population. Development of an epidermal growth factor receptor-directed biomarker selection strategy may optimize use of erlotinib in PS 2 patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Erlotinib monotherapy for stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer: a multicenter trial by the Korean Cancer Study Group.J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Sep;4(9):1136-43. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181b270a7. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19687764 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II trial of erlotinib monotherapy for pretreated elderly patients with advanced EGFR wild-type non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Res Notes. 2015 Jun 5;8:220. doi: 10.1186/s13104-015-1214-9. BMC Res Notes. 2015. PMID: 26043909 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of erlotinib for acquired resistance to gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Anticancer Res. 2014 Apr;34(4):1975-81. Anticancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24692734 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II study of erlotinib for chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer who are ineligible for platinum doublets.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011 Jan;67(1):35-9. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1280-6. Epub 2010 Feb 25. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 20182725 Clinical Trial.
-
A phase II study of erlotinib as initial treatment for patients with stage IIIB-IV non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2009 Feb;4(2):214-9. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181943bb9. J Thorac Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19179899 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Fatal toxic effects related to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors based on 53 cohorts with 9,569 participants.J Thorac Dis. 2020 Aug;12(8):4057-4069. doi: 10.21037/jtd-19-4000A. J Thorac Dis. 2020. PMID: 32944317 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors for elderly patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2010;2010:348174. doi: 10.1155/2010/348174. Epub 2010 Jun 20. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2010. PMID: 20672050 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib 'dosing-to-rash': a phase II intrapatient dose escalation and pharmacologic study of erlotinib in previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Br J Cancer. 2011 Sep 27;105(7):938-44. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.332. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21878940 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Durable complete remission of poor performance status metastatic lung adenocarcinoma patient treated with second-line erlotinib: a case report.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Sep 6;10:4347-4354. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S131756. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28919784 Free PMC article.
-
Erlotinib in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer: an update for clinicians.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2012 Jan;4(1):19-29. doi: 10.1177/1758834011427927. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22229045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Raez LE, Lilenbaum R. New developments in chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2006;18:156–61. - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA, Crowell R, Hensing TE, et al. Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, stage IV: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition) Chest. 2007;132:277s–289s. - PubMed
-
- Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:2452–50. - PubMed
-
- Blackhall FH, Bhosie J, Thatcher N. Chemotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with performance status 2. Curr Opin Oncol. 2005;17:135–9. - PubMed
-
- Devlin JG, Langer CJ. The 800-lb gorilla we all ignore: treatment of NSCLC in elderly and PS 2 patients. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2007;5:216–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-14028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-42777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA012644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-45461/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-68183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-63850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-46441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-11083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180846/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-04919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-45808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-32102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35128/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-45560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA042777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA011083/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-35178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-27057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-46368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA-38926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA068183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials