Dynein is required for polarized dendritic transport and uniform microtubule orientation in axons
- PMID: 18758451
- PMCID: PMC2588425
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb1777
Dynein is required for polarized dendritic transport and uniform microtubule orientation in axons
Abstract
Axons and dendrites differ in both microtubule organization and in the organelles and proteins they contain. Here we show that the microtubule motor dynein has a crucial role in polarized transport and in controlling the orientation of axonal microtubules in Drosophila melanogaster dendritic arborization (da) neurons. Changes in organelle distribution within the dendritic arbors of dynein mutant neurons correlate with a proximal shift in dendritic branch position. Dynein is also necessary for the dendrite-specific localization of Golgi outposts and the ion channel Pickpocket. Axonal microtubules are normally oriented uniformly plus-end-distal; however, without dynein, axons contain both plus- and minus-end distal microtubules. These data suggest that dynein is required for the distinguishing properties of the axon and dendrites: without dynein, dendritic organelles and proteins enter the axon and the axonal microtubules are no longer uniform in polarity.
Figures

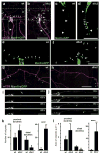
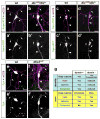
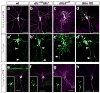
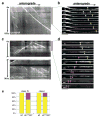
Comment in
-
Dynein branches out.Nat Cell Biol. 2008 Oct;10(10):1131-2. doi: 10.1038/ncb1008-1131. Nat Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18830220
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- K99 MH080599/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K99MH080599/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32-HD53199/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS040929/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R00 MH080599/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH084234/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- F32 MH075223/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32-MH75223/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HD053199/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047200/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS40929/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS47200/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040929/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

