Adenosine receptors: therapeutic aspects for inflammatory and immune diseases
- PMID: 18758473
- PMCID: PMC2568887
- DOI: 10.1038/nrd2638
Adenosine receptors: therapeutic aspects for inflammatory and immune diseases
Abstract
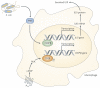
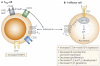
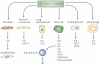
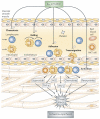
Adenosine is a key endogenous molecule that regulates tissue function by activating four G-protein-coupled adenosine receptors: A1, A2A, A2B and A3. Cells of the immune system express these receptors and are responsive to the modulatory effects of adenosine in an inflammatory environment. Animal models of asthma, ischaemia, arthritis, sepsis, inflammatory bowel disease and wound healing have helped to elucidate the regulatory roles of the various adenosine receptors in dictating the development and progression of disease. This recent heightened awareness of the role of adenosine in the control of immune and inflammatory systems has generated excitement regarding the potential use of adenosine-receptor-based therapies in the treatment of infection, autoimmunity, ischaemia and degenerative diseases.
Figures

References
-
- diMarco JP, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic use of adenosine in patients with supraventricular tachyarrhythmias. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985;6:417–425. - PubMed
-
- Travain MI, Wexler JP. Pharmacological stress testing. Semin. Nucl. Med. 1999;29:298–318. - PubMed
-
- Linden J. Molecular approach to adenosine receptors: receptor-mediated mechanisms of tissue protection. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2001;41:775–787. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

