Vav/Phospholipase Cgamma2-mediated control of a neutrophil-dependent murine model of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 18759305
- PMCID: PMC3004987
- DOI: 10.1002/art.23757
Vav/Phospholipase Cgamma2-mediated control of a neutrophil-dependent murine model of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: Accumulating evidence indicates an important role of neutrophils in the development of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Recruitment of neutrophils to the joint space and release of proteolytic enzymes can exacerbate tissue damage and the inflammatory response related to RA. Engagement of beta2 integrin and subsequent activation of downstream signaling have been shown to be fundamental for activation of neutrophil effector functions. The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis that Vav and phospholipase Cgamma2 (PLCgamma2), two molecules involved in integrin signaling, are required for arthritis generation and neutrophil activation in a mouse model of arthritis.
Methods: Arthritis was induced in wild-type (WT), Vav(null), and PLCgamma2(-/-) mice using the K/BxN serum-transfer model. Neutrophil function was assessed by analyses of adhesion, spreading, and degranulation on integrin-dependent substrates. Regulation of integrin signaling was determined by analyzing the phosphorylation of Pyk-2, Src, and ERK.
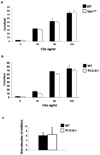
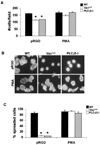
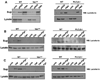
Results: Vav(null) and PLCgamma2(-/-) mice were protected from inflammation and bone erosion in the K/BxN serum-transfer model of arthritis. Mechanistically, Vav and PLCgamma2 control neutrophils mediated spreading and degranulation on integrin-dependent substrates. Consequently, the Vav/PLCgamma2 axis, acting downstream of the integrin receptor, modulated the activation of Pyk-2, Src, and ERK.
Conclusion: Our findings show that Vav cooperates with PLCgamma2 in modulating neutrophil activation downstream of the integrin receptor. This study identifies a Vav/PLCgamma2-dependent signaling pathway as a possible therapeutic target for the treatment of inflammation and bone disruption in arthritis.
Figures



References
-
- Ji H, Ohmura K, Mahmood U, Lee DM, Hofhuis FMA, Boackle SA, et al. Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity. 2002;16:157–168. - PubMed
-
- Walsh NC, Crotti TN, Goldring SR, Gravallese EM. Rheumatic diseases: the effects of inflammation on bone. Immunol Rev. 2005;208:228–251. - PubMed
-
- Wipke BT, Wang Z, Nagengast W, Reichert DE, Allen PM. Staging the initiation of autoantibody-induced arthritis: a critical role for immune complexes. J Immunol. 2004;172:7694–7702. - PubMed
-
- Burg ND, Pillinger MH. The neutrophil: function and regulation in innate and humoral immunity. Clin Immunol. 2001;99:7–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

