Regulation of NK cell responsiveness to achieve self-tolerance and maximal responses to diseased target cells
- PMID: 18759922
- PMCID: PMC3017429
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00658.x
Regulation of NK cell responsiveness to achieve self-tolerance and maximal responses to diseased target cells
Abstract
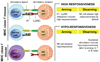
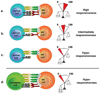
Inhibitory receptors specific for major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules govern the capacity of natural killer (NK) cells to attack class I-deficient cells ('missing-self recognition'). These receptors are expressed stochastically, such that the panel of expressed receptors varies between NK cells. This review addresses how the activity of NK cells is coordinated in the face of this variation to achieve a repertoire that is self-tolerant and optimally reactive with diseased cells. Recent studies show that NK cells arise in normal animals or humans that lack any known inhibitory receptors specific for self-MHC class I. These NK cells exhibit self-tolerance and exhibit functional hyporesponsiveness to stimulation through various activating receptors. Evidence suggests that hyporesponsiveness is induced because these NK cells cannot engage inhibitory MHC class I molecules and are therefore persistently over-stimulated by normal cells in the environment. Finally, we discuss evidence that hyporesponsiveness is a quantitative trait that varies depending on the balance of signals encountered by developing NK cells. Thus, a tuning process determines the functional set-point of NK cells, providing a basis for discriminating self from missing-self, and at the same time endowing each NK cell with the highest inherent responsiveness compatible with self-tolerance.
Figures

References
-
- Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. European Journal of Immunology. 1975;5:112–117. - PubMed
-
- Herberman RB, Nunn ME, Lavrin DH. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. International Journal of Cancer. 1975;16:216–229. - PubMed
-
- Becker S, Kiessling R, Lee N, Klein G. Modulation of sensitivity to natural killer cell lysis after in vitro explantation of a mouse lymphoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978;61:1495–1498. - PubMed
-
- Storkus WJ, Howell DN, Salter RD, Dawson JR, Cresswell P. NK susceptibility varies inversely with target cell class I HLA antigen expression. J. Immunol. 1987;138:1657–1659. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

